MOF@platelet-rich plasma antimicrobial GelMA dressing: structural characterization, bio-compatibility, and effect on wound healing efficacy
- PMID: 39309655
- PMCID: PMC11413862
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra04546g
MOF@platelet-rich plasma antimicrobial GelMA dressing: structural characterization, bio-compatibility, and effect on wound healing efficacy
Abstract
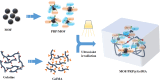
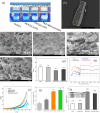
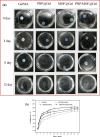
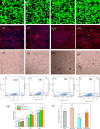
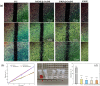
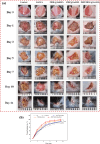
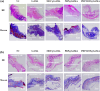
In this study, a metal-organic framework (MOF) antimicrobial gel loaded with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was prepared to improve the biological properties of gelatin gels and enhance their wound healing efficiency. PRP, MOF particles, and PRP-loaded MOF particles were each integrated into gelatin gels. The performance of the gels was evaluated for micro-structure, mechanical strength, in vitro bio-compatibility and pro-wound healing effects. The results revealed that the integration of PRP created a multi-cross-linked structure, increasing the ductility of the gels by over 40%. The addition of MOF particles significantly increased the strength of the gel from 13 kPa to 43 kPa. The combination of MOF and PRP further improved the cell induction and migration capabilities of the composite gel, and the scratches in the PRP/MOF@GelMA group had completely healed within 48 h. Due to the presence of MOF and PRP, the gel dressing exhibited inhibitory effects of 45.7% against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and 50.2% against Escherichia coli (E. coli). Different gels promoted tissue regeneration and wound healing ability of bacterial-infected wounds in C57 rats, while PRP/MOF@GelMA showed the strongest wound repair ability with 100% healing. This study provides a new strategy for the development and clinical application of gel dressings.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
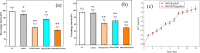
Similar articles
-
Preparation of biocompatible wound dressings with dual release of antibiotic and platelet-rich plasma for enhancing infected wound healing.J Biomater Appl. 2021 Aug;36(2):219-236. doi: 10.1177/0885328221996013. Epub 2021 Apr 14. J Biomater Appl. 2021. PMID: 33853425
-
[Effects of methacrylic anhydride gelatin hydrogel loaded with silver and recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor on deep partial-thickness burn wounds in rabbits].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022 Jul 20;38(7):640-649. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20210726-00260. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35899331 Chinese.
-
Enhanced Diabetic Rat Wound Healing by Platelet-Rich Plasma Adhesion Zwitterionic Hydrogel.Ann Plast Surg. 2024 Jan 1;92(1S Suppl 1):S2-S11. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003796. Ann Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38285989
-
The Efficiency and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Pers Med. 2023 Feb 27;13(3):430. doi: 10.3390/jpm13030430. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36983611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profound Properties of Protein-Rich, Platelet-Rich Plasma Matrices as Novel, Multi-Purpose Biological Platforms in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 19;25(14):7914. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147914. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

