NOP2-mediated 5-methylcytosine modification of APOL1 messenger RNA activates PI3K-Akt and facilitates clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression
- PMID: 39309431
- PMCID: PMC11414376
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.97503
NOP2-mediated 5-methylcytosine modification of APOL1 messenger RNA activates PI3K-Akt and facilitates clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression
Abstract
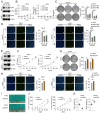
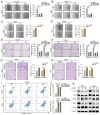
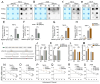
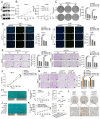
Background: By regulating the functions of multiple RNAs, 5-methylcytosine (m5C) RNA methylation, particularly mediated by NOP2, is involved in tumorigenesis and developments. However, the specific functions and potential mechanisms of m5C, especially involving NOP2, in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), remain unclear. Methods: NOP2 expression in cell lines and patient tissues was detected using western blotting, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), and immunohistochemistry. The biological effects of NOP2 on ccRCC cells were investigated through a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments. To explore the potential regulatory mechanisms by which NOP2 affects ccRCC progression, m5C bisulfite sequencing, RNA-sequencing, RNA immunoprecipitation and methylated RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP/MeRIP) RT-qPCR assay, luciferase reporter assay, RNA stability assay, and bioinformatic analysis were performed. Results: NOP2 expression was significantly upregulated in ccRCC tissues and was associated with poor prognosis. Moreover, loss-of-function and gain-of-function assays demonstrated that NOP2 altered ccRCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Mechanistically, NOP2 stimulated m5C modification of apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) mRNA, and m5C reader YBX1 stabilized APOL1 mRNA through recognizing and binding to m5C site in the 3'-untranslated regions. Silencing APOL1 expression inhibited ccRCC cell proliferation in vitro and tumor formation in vivo. Furthermore, NOP2/APOL1 affected ccRCC progression via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Conclusion: NOP2 functions as an oncogene in ccRCC by promoting tumor progression through the m5C-dependent stabilization of APOL1, which in turn regulates the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for ccRCC.
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine; APOL1; NOP2; clear cell renal cell carcinoma; clinical prognosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PLAUR facilitates the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.PeerJ. 2024 Jun 27;12:e17555. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17555. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38948215 Free PMC article.
-
IFI16 promotes the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through the IL6/PI3K/AKT axis.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 3;22(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05354-w. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38831470 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM26 inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression through destabilizing ETK and thus inactivation of AKT/mTOR signaling.J Transl Med. 2024 May 21;22(1):481. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05273-w. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38773612 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA‑205‑5p functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating VEGFA and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in renal carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2019 Nov;42(5):1677-1688. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7307. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31545453 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding PTEN regulation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Pathway for biomarker discovery and therapeutic insights.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Sep;1879(5):189165. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189165. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39117092 Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt JR, Finelli A. Landmarks in the diagnosis and treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Nature reviews Urology. 2014;11:517–25. - PubMed
-
- van der Mijn JC, Mier JW, Broxterman HJ, Verheul HM. Predictive biomarkers in renal cell cancer: insights in drug resistance mechanisms. Drug resistance updates: reviews and commentaries in antimicrobial and anticancer chemotherapy. 2014;17:77–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

