Regulatory effect of N6-methyladenosine on tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 39295872
- PMCID: PMC11408240
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1453774
Regulatory effect of N6-methyladenosine on tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
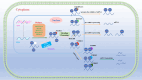
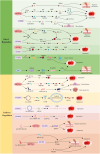
Previous studies have demonstrated that genetic alterations governing epigenetic processes frequently drive tumor development and that modifications in RNA may contribute to these alterations. In the 1970s, researchers discovered that N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent form of RNA modification in advanced eukaryotic messenger RNA (mRNA) and noncoding RNA (ncRNA). This modification is involved in nearly all stages of the RNA life cycle. M6A modification is regulated by enzymes known as m6A methyltransferases (writers) and demethylases (erasers). Numerous studies have indicated that m6A modification can impact cancer progression by regulating cancer-related biological functions. Tumor angiogenesis, an important and unregulated process, plays a pivotal role in tumor initiation, growth, and metastasis. The interaction between m6A and ncRNAs is widely recognized as a significant factor in proliferation and angiogenesis. Therefore, this article provides a comprehensive review of the regulatory mechanisms underlying m6A RNA modifications and ncRNAs in tumor angiogenesis, as well as the latest advancements in molecular targeted therapy. The aim of this study is to offer novel insights for clinical tumor therapy.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; angiogenesis; anti-tumor therapy; noncoding RNA; regulatory role; tumor.
Copyright © 2024 YuYan and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel insights into the interplay between m6A modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2020 Aug 7;19(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01233-2. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32767982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-talk among writers, readers, and erasers of m6A regulates cancer growth and progression.Sci Adv. 2018 Oct 3;4(10):eaar8263. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar8263. eCollection 2018 Oct. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 30306128 Free PMC article.
-
m6A modification in non-coding RNAs: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications in fibrosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117331. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117331. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39191030 Review.
-
N6 -methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification in human cancer.Cell Prolif. 2020 Nov;53(11):e12921. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12921. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 33029866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Modification and Its Regulators in Male Reproduction].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):527-534. doi: 10.12182/20240560103. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948273 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

