Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental approaches of the anti-proliferative effects of Rhamnus prinoides ethyl-acetate extract in cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 39290290
- PMCID: PMC11407055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37324
Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental approaches of the anti-proliferative effects of Rhamnus prinoides ethyl-acetate extract in cervical cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer, one of the lethal cancers among women, is a challenging disease to treat. The current therapies often come with severe side effects and the risk of resistance development. Traditional herbal medicine, with its potential to offer effective and less toxic options, is a promising avenue. This study was undertaken to investigate the potential of Rhamnus prinoides (R. prinoides) root bark extracts in selectively inhibiting the proliferation of cervical cancer cells, using the HeLa cell line as an in vitro model.
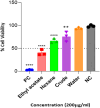
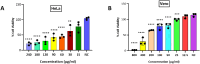
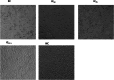
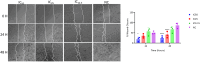
Methods: R. prinoides plant extracts were first screened at a fixed concentration of 200 μg/ml to determine the active extract. The selective anti-proliferative activity of the active extract was evaluated in a concentration dilution assay using the (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) MTT assay on cancerous (HeLa) cells and non-cancerous (Vero) cells to determine the half-maximal inhibitory (IC50) and half-cytotoxic concentrations (CC50), respectively. Functional assays on cell morphology (by microscopy), cell migration (wound healing assay) and cell cycle (by flow cytometry) were also conducted. The active extract was analyzed using Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) to determine any compounds it contained. Following identification of possible gene targets by network pharmacology, the genes were validated by molecular docking and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR).
Results: The ethyl acetate extract of R. prinoides (EARP), the most active extract, selectively inhibited the growth of cervical cancer cells, their migration and induced cell cycle arrest at the S phase. In silico analysis revealed that squalene, 3,3a,6,6-tetramethyl-4,5,5a,7,8,9-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[i]indene and Olean-12-en-3.beta.-ol, acetate showed acceptable drug-like characteristics and may be partly attributed to the bioactivity demonstrated and the deregulation of the mRNA expression of AKT1, NF-κB, p53, Bax, Bcl-2, and Er-b-B2.
Conclusion: This study, for the first time, demonstrates the anti-proliferation effects of EARP and forms a firm foundation for further drug development studies.
Keywords: Anti-proliferative activity; Cervical cancer; Cytotoxicity; Network pharmacology; Rhamnus prinoides.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemical analysis, in-vitro and in-silico study of antiproliferative activity of ethyl acetate fraction of Launaea cornuta (Hochst. ex Oliv. & Hiern) C. Jeffrey against human cervical cancer cell line.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1399885. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1399885. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39005932 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the wound healing activity of the crude extract of root bark of Brucea antidysentrica, the leaves of Dodonaea angustifolia and Rhamnus prinoides in mice.Heliyon. 2021 Jan 19;7(1):e05901. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e05901. eCollection 2021 Jan. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33521349 Free PMC article.
-
Rhamnus prinoides (gesho): A source of diverse anti-biofilm activity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;241:111955. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111955. Epub 2019 May 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31102615
-
GC-MS analysis, molecular docking, and apoptotic-based cytotoxic effect of Caladium lindenii Madison extracts toward the HeLa cervical cancer cell line.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 8;14(1):18438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69582-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39117897 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression and anticancer evaluation of Kigelia africana (Lam.) Benth. Extracts using MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 5;19(6):e0303134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303134. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38837975 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

