Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Patient With Advanced Breast Cancer Treated With Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors and Endocrine Therapy
- PMID: 39286469
- PMCID: PMC11405092
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.69548
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Patient With Advanced Breast Cancer Treated With Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors and Endocrine Therapy
Abstract
This case shares the case of a post-menopausal woman who develops Philadelphia chromosome-positive B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) while receiving treatment for invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) of the breast. The patient received a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor + aromatase inhibitor (AI) for the IDC; hyperfractionate cyclophosphamide, vincristine sulfate, doxorubicin hydrochloride (Adriamycin), methotrexate, and cytarabine (hyperCVAD), and the steroid hormone dexamethasone were added to treat the B-ALL. HyperCVAD combined with CDK 4/6 inhibitor + AI was very well tolerated. The CDK 4/6 inhibitor and AI were only held once in the treatment course due to adverse effect (AE) intolerance. The patient remains on a CDK 4/6 inhibitor and ponatinib with only low-grade fatigue as an AE. This case underscores the importance of a concurrent approach to managing hematologic and breast malignancies. The combined treatment regimens were effective and well-tolerated. Vigilant follow-up is essential for patients in remission from both malignancies, ensuring effective disease surveillance and treatment management. Integrated care remains pivotal for optimal outcomes.
Keywords: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; aromatase inhibitor therapy; b-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; breast cancer management; cdk 4/6 inhibitors.
Copyright © 2024, Bailey et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. UT Health San Antonio IRB issued approval STUDY00000714. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
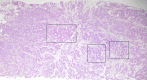
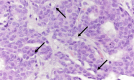


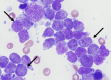
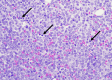
Similar articles
-
Combination of hyper-CVAD with ponatinib as first-line therapy for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: long-term follow-up of a single-centre, phase 2 study.Lancet Haematol. 2018 Dec;5(12):e618-e627. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30176-5. Lancet Haematol. 2018. PMID: 30501869 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combination of hyper-CVAD with ponatinib as first-line therapy for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a single-centre, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2015 Nov;16(15):1547-1555. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00207-7. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Lancet Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26432046 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Final report of a phase II study of imatinib mesylate with hyper-CVAD for the front-line treatment of adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Haematologica. 2015 May;100(5):653-61. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.118588. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 25682595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Review of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer.Ann Pharmacother. 2019 Feb;53(2):195-203. doi: 10.1177/1060028018793656. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Ann Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30079740 Review.
-
Management of Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the current era.Curr Res Transl Med. 2023 Apr-Jun;71(2):103392. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2023.103392. Epub 2023 Apr 23. Curr Res Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37121211 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
