Bis-chalcones obtained via one-pot synthesis as the anti-neurodegenerative agents and their effect on the HT-22 cell line
- PMID: 39286165
- PMCID: PMC11403034
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37147
Bis-chalcones obtained via one-pot synthesis as the anti-neurodegenerative agents and their effect on the HT-22 cell line
Abstract
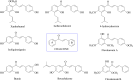
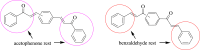
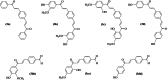
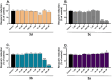
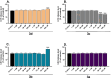
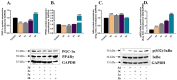
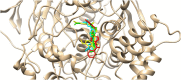
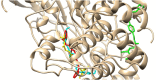
In the area of research on neurodegenerative diseases, the current challenge is to search for appropriate research methods that would detect these diseases at the earliest possible stage, but also new active structures that would reduce the rate of the disease progression and minimize the intensity of their symptoms experienced by the patient. The chalcones are considered in the context of candidates for new drugs dedicated to the fight against neurodegenerative diseases. The synthesis of bis-chalcone derivatives (3a-3d), as aim molecules was performed. Their structures were established by applying 1H NMR, 13C NMR, MS, FT-IR and UV-Vis spectra. All bis-chalcones were synthesized from terephthalaldehyde and appropriate aromatic ketone as substrates in the Claisen-Schmidt condensation method and evaluated in the biological tests and in silico analysis. Compounds exerted antioxidant activity using the HORAC method (3a-3d) and decreased the activities of GPx, COX-2 (3b-3d), GR (3a-3c) and CAT (3a,3b). The high anti-neurodegenerative potential of all four bis-chalcones was observed by inhibition of acetyl- (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and a positive effect on the mouse hippocampal neuronal HT-22 cell line (LDH release and PGC-1α, PPARγ and GAPDH protein expression). TD-DFT method (computing a number of descriptors associated with HOMO-LUMO electron transition: electronegativity, chemical hardness and potential, first ionization potential, electron affinity) was employed to study the spectroscopic properties. This method showed that the first excited state of compounds was consistent with their maximum absorption in the computed UV-Vis spectra, which showed good agreement with the experimental spectrum using PBE1PBE functional. Using in silico approach, interactions of bis-chalcones with selected targets (aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) PAS-A Domain, ligand binding domain of human PPAR-γ, soman-aged human BChE-butyrylthiocholine complex, Torpedo californica AChE:N-piperidinopropyl-galanthamine complex and the COX-2-celecoxib complex) were characterized. Results obtained in in silico models were consistent with in vitro experiments.
Keywords: Anti-neurodegenerative activity; Bis-chalcones; Claisen-Schmidt reaction; Cytotoxicity; Molecular docking.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
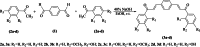

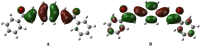
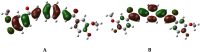
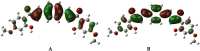
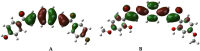
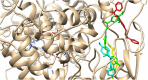
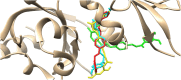

Similar articles
-
Synthesis of bis-Chalcones Based on Green Chemistry Strategies and Their Cytotoxicity Toward Human MeWo and A375 Melanoma Cell Lines.Molecules. 2024 Oct 31;29(21):5171. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215171. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519811 Free PMC article.
-
Chalcones bearing nitrogen-containing heterocyclics as multi-targeted inhibitors: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies.J Mol Recognit. 2023 Jul;36(7):e3020. doi: 10.1002/jmr.3020. Epub 2023 May 5. J Mol Recognit. 2023. PMID: 37092742
-
Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of novel chalcone, heterochalcone and bis-chalcone derivatives and the evaluation of their antioxidant properties and as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Sep;90:103034. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103034. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31280015
-
Bis-chalcones: A review of synthetic methodologies and anti-inflammatory effects.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Apr 5;252:115280. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115280. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36966653 Review.
-
Recent developments in biological aspects of chalcones: the odyssey continues.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019 Mar;14(3):249-288. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2019.1573812. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019. PMID: 30773996 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of bis-Chalcones Based on Green Chemistry Strategies and Their Cytotoxicity Toward Human MeWo and A375 Melanoma Cell Lines.Molecules. 2024 Oct 31;29(21):5171. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215171. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soobrattee M.A., Neergheen V.S., Luximon-Ramma A., Aruoma O.I., Bahorun T. Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: mechanism and actions. Mutat. Res. 2005;11(579):200–213. https://doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.03.023 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szwajgier D., Baranowska-Wójcik E., Kukula-Koch W., Kowalik K., Polak-Berecka M., Waśko A. Evolution of the anticholinesterase, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activity of Epilobium angustifolium L. infusion during in vitro digestion. J. Funct.Foods. 2021;85 doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104645. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

