Advancements and challenges in mRNA and ribonucleoprotein-based therapies: From delivery systems to clinical applications
- PMID: 39281702
- PMCID: PMC11402252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102313
Advancements and challenges in mRNA and ribonucleoprotein-based therapies: From delivery systems to clinical applications
Abstract
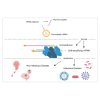
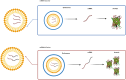
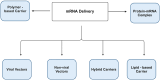
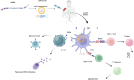
The use of mRNA and ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) as therapeutic agents is a promising strategy for treating diseases such as cancer and infectious diseases. This review provides recent advancements and challenges in mRNA- and RNP-based therapies, focusing on delivery systems such as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), which ensure efficient delivery to target cells. Strategies such as microfluidic devices are employed to prepare LNPs loaded with mRNA and RNPs, demonstrating effective genome editing and protein expression in vitro and in vivo. These applications extend to cancer treatment and infectious disease management, with promising results in genome editing for cancer therapy using LNPs encapsulating Cas9 mRNA and single-guide RNA. In addition, tissue-specific targeting strategies offer potential for improved therapeutic outcomes and reduced off-target effects. Despite progress, challenges such as optimizing delivery efficiency and targeting remain. Future research should enhance delivery efficiency, explore tissue-specific targeting, investigate combination therapies, and advance clinical translation. In conclusion, mRNA- and RNP-based therapies offer a promising avenue for treating various diseases and have the potential to revolutionize medicine, providing new hope for patients worldwide.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; LNPs; MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications; RNP; delivery systems; genome editing; mRNA.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A biodegradable lipid nanoparticle delivers a Cas9 ribonucleoprotein for efficient and safe in situ genome editing in melanoma.Acta Biomater. 2024 Oct 25:S1742-7061(24)00622-6. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.10.030. Online ahead of print. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39461690
-
Comparative analysis of lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 RNP versus mRNA/sgRNA for gene editing in vitro and in vivo.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024 Mar;196:114207. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114207. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024. PMID: 38325664
-
Developing Biodegradable Lipid Nanoparticles for Intracellular mRNA Delivery and Genome Editing.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Nov 2;54(21):4001-4011. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00500. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34668716 Review.
-
Finely tuned ionizable lipid nanoparticles for CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein delivery and gene editing.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Apr 12;22(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02427-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38609947 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies in the delivery of Cas9 ribonucleoprotein for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):614-648. doi: 10.7150/thno.47007. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sahin U., Karikó K., Türeci Ö. mRNA-based therapeutics—developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014;13:759–780. - PubMed
-
- Caruthers M.H. A brief review of DNA and RNA chemical synthesis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011;39:575–580. - PubMed
-
- Thiel V., Herold J., Schelle B., Siddell S.G. Infectious RNA transcribed in vitro from a cDNA copy of the human coronavirus genome cloned in vaccinia virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2001;82:1273–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

