Changing impact of dietary risk factors on cardiovascular mortality in 46 European countries from 1990 to 2019 by age and sex: A data article of the GBD Study
- PMID: 39281011
- PMCID: PMC11395748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110851
Changing impact of dietary risk factors on cardiovascular mortality in 46 European countries from 1990 to 2019 by age and sex: A data article of the GBD Study
Abstract
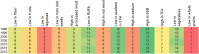
This study aimed to estimate the association between single dietary risk factors and cardiovascular mortality in the WHO European Region, its four subregions and 46 individual countries. For this purpose, data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study (GBD) 2019 iteration were employed and analysed according to age (≥ 25 years) and sex. The comparative risk assessment framework of the GBD was utilized in order to estimate the number of cardiovascular deaths that could be attributed to 13 dietary risks. The study period spanned from 1990 to 2019. Between 1990 and 2019 the absolute number of diet-related cardiovascular deaths (DRCDs) in the WHO ER decreased from 1.69 to 1.55 million deaths. Moreover, a decline in the absolute number of deaths was observed in two subregions and 27 countries. In 2019, the number of deaths was almost equally distributed between women and men. This distribution has undergone only slight temporal changes. The number of cases for men were found to be higher in three subregions and in 30 countries. The majority of DRCDs in the WHO ER were attributable to 'a diet low in whole grains', which was also the primary risk factor in three subregions und 29 countries. The next most-common risk factor was 'a diet low in legumes', followed by 'a diet high in sodium'. In particular, the risk factor 'a diet high in sodium' was a significant contributing factor in Central Europe. In addition, the risk factor 'a diet high in red meat' was more pronounced in Western Europe than in the other regions and slightly more influential in the group of women across all regions. For men 'a diet high in sodium' was more prominent than for women. In essence, slight changes in the influence of individual risk factors were observed across the different age groups. The datasheets enable the observation of changes within the dietary risks over time, their distribution by age and sex, and differences between regions and individual countries in detail. This allows for an individual assessment of the problem situation for each country, the subregions and the European Region as a whole, with the aim of developing solution strategies based on this assessment. Dietary interventions can focus on the relevant food and target groups in order to support a health-promoting diet.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Europe; Nutrition; Public health.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular mortality attributable to dietary risk factors in 54 countries in the WHO European Region from 1990 to 2019: an updated systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024 Apr 15:zwae136. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae136. Online ahead of print. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38620078
-
Cardiovascular mortality attributable to dietary risk factors in 51 countries in the WHO European Region from 1990 to 2016: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study.Eur J Epidemiol. 2019 Jan;34(1):37-55. doi: 10.1007/s10654-018-0473-x. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Eur J Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 30547256 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.Lancet. 2015 Dec 5;386(10010):2287-323. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00128-2. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 26364544 Free PMC article.
-
Excess Mortality from Mental, Neurological, and Substance Use Disorders in the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010.In: Patel V, Chisholm D, Dua T, Laxminarayan R, Medina-Mora ME, editors. Mental, Neurological, and Substance Use Disorders: Disease Control Priorities, Third Edition (Volume 4). Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2016 Mar 14. Chapter 3. In: Patel V, Chisholm D, Dua T, Laxminarayan R, Medina-Mora ME, editors. Mental, Neurological, and Substance Use Disorders: Disease Control Priorities, Third Edition (Volume 4). Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2016 Mar 14. Chapter 3. PMID: 27227239 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The 2023 Latin America report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: the imperative for health-centred climate-resilient development.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Apr 23;33:100746. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100746. eCollection 2024 May. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 38800647 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pörschmann T., Meier T., Lorkowski S. Cardiovascular mortality attributable to dietary risk factors in 54 countries in the WHO European Region from 1990 to 2019: an updated systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024 doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae136. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources