The Dependence of NiMo/Cu Catalyst Composition on Its Catalytic Activity in Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis Reactions
- PMID: 39274743
- PMCID: PMC11396714
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17174353
The Dependence of NiMo/Cu Catalyst Composition on Its Catalytic Activity in Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis Reactions
Abstract
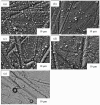
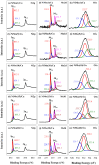
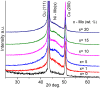
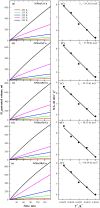
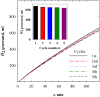
The production of high-purity hydrogen from hydrogen storage materials with further direct use of generated hydrogen in fuel cells is still a relevant research field. For this purpose, nickel-molybdenum-plated copper catalysts (NiMo/Cu), comprising between 1 and 20 wt.% molybdenum, as catalytic materials for hydrogen generation, were prepared using a low-cost, straightforward electroless metal deposition method by using citrate plating baths containing Ni2+-Mo6+ ions as a metal source and morpholine borane as a reducing agent. The catalytic activity of the prepared NiMo/Cu catalysts toward alkaline sodium borohydride (NaBH4) hydrolysis increased with the increase in the content of molybdenum present in the catalysts. The hydrogen generation rate of 6.48 L min-1 gcat-1 was achieved by employing NiMo/Cu comprising 20 wt.% at a temperature of 343 K and a calculated activation energy of 60.49 kJ mol-1 with remarkable stability, retaining 94% of its initial catalytic activity for NaBH4 hydrolysis following the completion of the fifth cycle. The synergetic effect between nickel and molybdenum, in addition to the formation of solid-state solutions between metals, promoted the hydrogen generation reaction.
Keywords: H2 production; boron-hydride; catalysis; electroless plating; non-noble metals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Copper Nanowires as Highly Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for Rapid Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jun 12;10(6):1153. doi: 10.3390/nano10061153. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545513 Free PMC article.
-
Graphene-Modified Co-B-P Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Aug 9;12(16):2732. doi: 10.3390/nano12162732. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36014597 Free PMC article.
-
Facile green synthesis of a novel NiO and its catalytic effect on methylene blue photocatalytic reduction and sodium borohydride hydrolysis.Int J Phytoremediation. 2024;26(10):1577-1592. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2024.2338470. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Int J Phytoremediation. 2024. PMID: 38634226
-
Enhancing hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis and the role of a Co/CuFe2O4 nanocatalyst in a continuous flow system.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 26;14(1):9659. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60428-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38671177
-
Emerging trends in research and development on earth abundant materials for ammonia degradation coupled with H2 generation.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2024 Jan 9;25(1):2301423. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2023.2301423. eCollection 2024. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 38357414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alasali F., Abuashour M.I., Hammad W., Almomani D., Obeidat A.M., Holderbaum W. A review of hydrogen production and storage materials for efficient integrated hydrogen energy systems. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024;12:1934–1968. doi: 10.1002/ese3.1723. - DOI
-
- Ramachandran R., Menon R.K. An overview of industrial uses of hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 1998;23:593–598. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(97)00112-2. - DOI
-
- [(accessed on 22 August 2024)]. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/low-emission-fuels/hydrogen.
-
- Guan D., Wang B., Zhang J., Shi R., Jiao K., Li L., Wang Y., Xie B., Zhang Q., Yu J., et al. Hydrogen society: From present to future. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023;16:4926–4943. doi: 10.1039/D3EE02695G. - DOI
-
- Ball M., Wietschel M. The future of hydrogen—Opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2009;34:615–627. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.11.014. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

