Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 39274263
- PMCID: PMC11396415
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13175050
Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
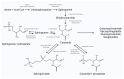
Sphingolipids (SLs) are bioactive signaling molecules essential for various cellular processes, including cell survival, proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. Key SLs such as ceramides, sphingosine, and their phosphorylated forms play critical roles in cellular integrity. Dysregulation of SL levels is implicated in numerous diseases, notably chronic kidney disease (CKD). This review focuses on the role of SLs in CKD, highlighting their potential as biomarkers for early detection and prognosis. SLs maintain renal function by modulating the glomerular filtration barrier, primarily through the activity of podocytes. An imbalance in SLs can lead to podocyte damage, contributing to CKD progression. SL metabolism involves complex enzyme-catalyzed pathways, with ceramide serving as a central molecule in de novo and salvage pathways. Ceramides induce apoptosis and are implicated in oxidative stress and inflammation, while sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) promotes cell survival and vascular health. Studies have shown that SL metabolism disorders are linked to CKD progression, diabetic kidney disease, and glomerular diseases. Targeting SL pathways could offer novel therapeutic approaches for CKD. This review synthesizes recent research on SL signaling regulation in kidney diseases, emphasizing the importance of maintaining SL balance for renal health and the potential therapeutic benefits of modulating SL pathways.
Keywords: ceramides; chronic kidney disease; sphingolipids; sphinogosine-1-phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Dietary Sphingolipids on Intestinal Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Immune Homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2021 May 14;12:635704. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.635704. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids in Genetic and Acquired Forms of Chronic Kidney Diseases.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(12):1238-1275. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170112114525. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28078995 Review.
-
The antithetic role of ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in cardiac dysfunction.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Jul;236(7):4857-4873. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30235. Epub 2021 Jan 11. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33432663 Review.
-
Signaling and regulatory functions of bioactive sphingolipids as therapeutic targets in multiple sclerosis.Neurochem Res. 2012 Jun;37(6):1154-69. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0728-y. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22451227 Review.
-
Alteration of Sphingolipids in Biofluids: Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 21;20(14):3564. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143564. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31330872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaabia Z., Poirier J., Moughaizel M., Aguesse A., Billon-Crossouard S., Fall F., Durand M., Dagher E., Krempf M., Croyal M. Plasma lipidomic analysis reveals strong similarities between lipid fingerprints in human, hamster and mouse compared to other animal species. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:15893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34329-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources