TP53 Mutation-Mediated Immune Evasion in Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 39272927
- PMCID: PMC11393945
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16173069
TP53 Mutation-Mediated Immune Evasion in Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
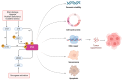
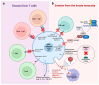
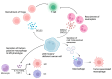
Mutation in p53 is the most frequent event in cancer development and a leading cause of cancer therapy resistance due to evasion of the apoptosis cascade. Beyond chemotherapies and radiation therapies, growing evidence indicates that p53-mutant tumors are resistant to a broad range of immune-based therapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). This highlights the role of p53 mutations in driving immune evasion of tumor cells. In this review, we first summarize recent studies revealing mechanisms by which p53-mutant tumors evade immune surveillance from T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and macrophages. We then review how these mutant tumor cells reshape the tumor microenvironment (TME), modulating bystander cells such as macrophages, neutrophils, and regulatory T (Treg) cells to foster immunosuppression. Additionally, we review clinical observations indicative of immune evasion associated with p53 loss or mutations. Finally, we discuss therapeutic strategies to enhance immune response in p53 wild-type (WT) or mutant tumors.
Keywords: immune evasion; immunotherapy; mouse double minute 2; p53; p53 mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cancer Stem Cells: Emerging Key Players in Immune Evasion of Cancers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 21;9:692940. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.692940. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34235155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting WEE1/AKT Restores p53-Dependent Natural Killer-Cell Activation to Induce Immune Checkpoint Blockade Responses in "Cold" Melanoma.Cancer Immunol Res. 2022 Jun 3;10(6):757-769. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-21-0587. Cancer Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35439317 Free PMC article.
-
TP53/mTORC1-mediated bidirectional regulation of PD-L1 modulates immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Nov 29;11(11):e007479. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007479. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38030304 Free PMC article.
-
Combining epigenetic and immune therapy to overcome cancer resistance.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Oct;65:99-113. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.019. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 31877341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune evasion in cell-based immunotherapy: unraveling challenges and novel strategies.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jan 12;31(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-00998-8. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38217016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Olivier M., Langerød A., Carrieri P., Bergh J., Klaar S., Eyfjord J., Theillet C., Rodriguez C., Lidereau R., BièChe I., et al. The clinical value of somatic TP53 gene mutations in 1,794 patients with breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:1157–1167. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1029. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

