Vangl2 suppresses NF-κB signaling and ameliorates sepsis by targeting p65 for NDP52-mediated autophagic degradation
- PMID: 39269442
- PMCID: PMC11398866
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.87935
Vangl2 suppresses NF-κB signaling and ameliorates sepsis by targeting p65 for NDP52-mediated autophagic degradation
Abstract
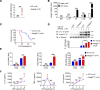
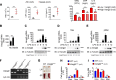
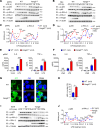
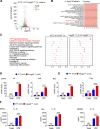
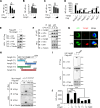
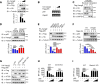
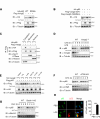
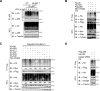
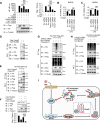
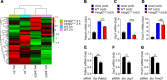
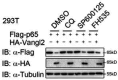
Van Gogh-like 2 (Vangl2), a core planar cell polarity component, plays an important role in polarized cellular and tissue morphology induction, growth development, and cancer. However, its role in regulating inflammatory responses remains elusive. Here, we report that Vangl2 is upregulated in patients with sepsis and identify Vangl2 as a negative regulator of The nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) signaling by regulating the protein stability and activation of the core transcription component p65. Mice with myeloid-specific deletion of Vangl2 (Vangl2ΔM) are hypersusceptible to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced septic shock. Vangl2-deficient myeloid cells exhibit enhanced phosphorylation and expression of p65, therefore, promoting the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines after LPS stimulation. Mechanistically, NF-κB signaling-induced-Vangl2 recruits E3 ubiquitin ligase PDLIM2 to catalyze K63-linked ubiquitination on p65, which serves as a recognition signal for cargo receptor NDP52-mediated selective autophagic degradation. Taken together, these findings demonstrate Vangl2 as a suppressor of NF-κB-mediated inflammation and provide insights into the crosstalk between autophagy and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: NF-κB signaling; PDLIM2; Vangl2; human; immunology; inflammation; mouse; selective autophagy; ubiquitin.
© 2023, Lu, Zhang, Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JL, JZ, HJ, ZH, YZ, LH, JY, YX, DW, HL, KZ, PT, QX, ZS, CP, XB, XY No competing interests declared
Figures


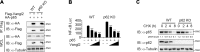
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.03.30.534894
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.87935.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.87935.2
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.87935.3
Similar articles
-
PDLIM7 Synergizes With PDLIM2 and p62/Sqstm1 to Inhibit Inflammatory Signaling by Promoting Degradation of the p65 Subunit of NF-κB.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 4;11:1559. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01559. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849529 Free PMC article.
-
HSP70 mediates degradation of the p65 subunit of nuclear factor κB to inhibit inflammatory signaling.Sci Signal. 2014 Dec 16;7(356):ra119. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005533. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 25515536
-
MKRN2 is a novel ubiquitin E3 ligase for the p65 subunit of NF-κB and negatively regulates inflammatory responses.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 5;7:46097. doi: 10.1038/srep46097. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28378844 Free PMC article.
-
PDLIM2-mediated termination of transcription factor NF-kappaB activation by intranuclear sequestration and degradation of the p65 subunit.Nat Immunol. 2007 Jun;8(6):584-91. doi: 10.1038/ni1464. Epub 2007 Apr 29. Nat Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17468759
-
Deubiquitinases in the regulation of NF-κB signaling.Cell Res. 2011 Jan;21(1):22-39. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.166. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21119682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression Profiles of Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Articular Cartilage of Rats Exposed to T-2 Toxin.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 5;24(18):13703. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813703. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762015 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

