Molecular mechanisms of Sepsis attacking the immune system and solid organs
- PMID: 39267971
- PMCID: PMC11390691
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1429370
Molecular mechanisms of Sepsis attacking the immune system and solid organs
Abstract
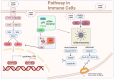
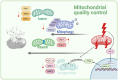
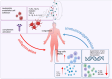
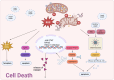
Remarkable progress has been achieved in sepsis treatment in recent times, the mortality rate of sepsis has experienced a gradual decline as a result of the prompt administration of antibiotics, fluid resuscitation, and the implementation of various therapies aimed at supporting multiple organ functions. However, there is still significant mortality and room for improvement. The mortality rate for septic patients, 22.5%, is still unacceptably high, accounting for 19.7% of all global deaths. Therefore, it is crucial to thoroughly comprehend the pathogenesis of sepsis in order to enhance clinical diagnosis and treatment methods. Here, we summarized classic mechanisms of sepsis progression, activation of signal pathways, mitochondrial quality control, imbalance of pro-and anti- inflammation response, diseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), cell death, presented the latest research findings for each mechanism and identify potential therapeutic targets within each mechanism.
Keywords: apoptosis; inflammation; mechanism; pathogenesis; pyroptosis; sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Gao, Zhao, Lv and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sepsis Care Pathway 2019.Qatar Med J. 2019 Nov 7;2019(2):4. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2019.qccc.4. eCollection 2019. Qatar Med J. 2019. PMID: 31763206 Free PMC article.
-
[Advance in sepsis-related coagulation disorders and immunity response].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Dec;33(12):1519-1523. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201120-00723. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 35131024 Review. Chinese.
-
[Research progress on the role of pyroptosis in sepsis-related coagulation disorder].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jul;36(7):768-773. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230901-00735. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39223895 Review. Chinese.
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acid-derived lipid mediator Resolvin D1 alleviates sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation via Caspase-1/Gasdermin D pyroptotic pathway.Clin Nutr. 2024 Jun;43(6):1372-1383. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.04.020. Epub 2024 Apr 20. Clin Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38678822
-
Pathophysiology of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Sepsis: A Clinically Focused Overview.Cells. 2023 Aug 22;12(17):2120. doi: 10.3390/cells12172120. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shankar-Hari M, Phillips GS, Levy ML, Seymour CW, Liu VX, Deutschman CS, et al. . Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: for the third international consensus definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:775–87. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0289, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

