Altered firing output of VIP interneurons and early dysfunctions in CA1 hippocampal circuits in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39264364
- PMCID: PMC11392531
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.95412
Altered firing output of VIP interneurons and early dysfunctions in CA1 hippocampal circuits in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
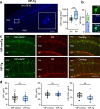
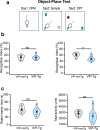
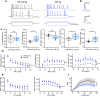
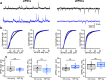
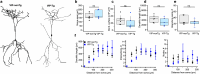
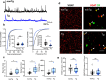
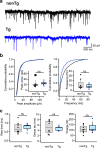
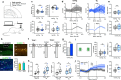
Alzheimer's disease (AD) leads to progressive memory decline, and alterations in hippocampal function are among the earliest pathological features observed in human and animal studies. GABAergic interneurons (INs) within the hippocampus coordinate network activity, among which type 3 interneuron-specific (I-S3) cells expressing vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and calretinin play a crucial role. These cells provide primarily disinhibition to principal excitatory cells (PCs) in the hippocampal CA1 region, regulating incoming inputs and memory formation. However, it remains unclear whether AD pathology induces changes in the activity of I-S3 cells, impacting the hippocampal network motifs. Here, using young adult 3xTg-AD mice, we found that while the density and morphology of I-S3 cells remain unaffected, there were significant changes in their firing output. Specifically, I-S3 cells displayed elongated action potentials and decreased firing rates, which was associated with a reduced inhibition of CA1 INs and their higher recruitment during spatial decision-making and object exploration tasks. Furthermore, the activation of CA1 PCs was also impacted, signifying early disruptions in CA1 network functionality. These findings suggest that altered firing patterns of I-S3 cells might initiate early-stage dysfunction in hippocampal CA1 circuits, potentially influencing the progression of AD pathology.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; circuit; disinhibition; hippocampus; inhibition; memory; mouse; neuroscience.
© 2024, Michaud, Francavilla et al.
Conflict of interest statement
FM, RF, DT, PI, ST, FC, LT No competing interests declared
Figures
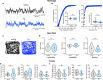
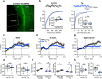
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2024.01.12.575331
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.95412.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.95412.2
Similar articles
-
Early alterations in hippocampal perisomatic GABAergic synapses and network oscillations in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease amyloidosis.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 15;14(1):e0209228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209228. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30645585 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Mechanisms Underlying the Network State-Dependent Recruitment of VIP-Expressing Interneurons in the CA1 Hippocampus.Cereb Cortex. 2020 May 18;30(6):3667-3685. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhz334. Cereb Cortex. 2020. PMID: 32080739 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal neural circuit connectivity alterations in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model revealed by monosynaptic rabies virus tracing.Neurobiol Dis. 2022 Oct 1;172:105820. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105820. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Neurobiol Dis. 2022. PMID: 35843448 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory circuits in fear memory and fear-related disorders.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Mar 23;17:1122314. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1122314. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 37035504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Learning from inhibition: Functional roles of hippocampal CA1 inhibition in spatial learning and memory.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;76:102604. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102604. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35810533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protocol for synchronized wireless fiber photometry and video recordings in rodents during behavior.STAR Protoc. 2024 Dec 20;5(4):103407. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.103407. Epub 2024 Oct 18. STAR Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39425933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Algamal M, Russ AN, Miller MR, Hou SS, Maci M, Munting LP, Zhao Q, Gerashchenko D, Bacskai BJ, Kastanenka KV. Reduced excitatory neuron activity and interneuron-type-specific deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Communications Biology. 2022;5:1323. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04268-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

