The mRNA dynamics underpinning translational control mechanisms of Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis
- PMID: 39263986
- PMCID: PMC11555706
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20231293
The mRNA dynamics underpinning translational control mechanisms of Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis
Abstract
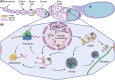
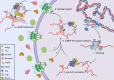
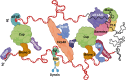
Advances in the study of mRNAs have yielded major new insights into post-transcriptional control of gene expression. Focus on the spatial regulation of mRNAs in highly polarized cells has demonstrated that mRNAs translocate through cells as mRNA:protein granules (mRNPs). These complex self-assemblies containing nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins are fundamental to the coordinated translation throughout cellular development. Initial studies on translational control necessitated fixed tissue, but the last 30 years have sparked innovative live-cell studies in several cell types to deliver a far more nuanced picture of how mRNA-protein dynamics exert translational control. In this review, we weave together the events that underpin mRNA processes and showcase the pivotal studies that revealed how a multitude of protein factors engage with a transcript. We highlight a mRNA's ability to act as a 'super scaffold' to facilitate molecular condensate formation and further moderate translational control. We focus on the Drosophila melanogaster germline due to the extensive post-transcriptional regulation occurring during early oogenesis. The complexity of the spatio-temporal expression of maternal transcripts in egg chambers allows for the exploration of a wide range of mechanisms that are crucial to the life cycle of mRNAs.
Keywords: Drosophila oogenesis; oskar; P bodies; condensates; mRNA translational control; post transcriptional gene expression regulation.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cup is essential for oskar mRNA translational repression during early Drosophila oogenesis.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):573-587. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2242650. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37553798 Free PMC article.
-
Cup regulates oskar mRNA stability during oogenesis.Dev Biol. 2017 Jan 1;421(1):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.06.040. Epub 2016 Aug 21. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27554167
-
The Drosophila fragile X protein functions as a negative regulator in the orb autoregulatory pathway.Dev Cell. 2005 Mar;8(3):331-42. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.011. Dev Cell. 2005. PMID: 15737929
-
Localization, anchoring and translational control of oskar, gurken, bicoid and nanos mRNA during Drosophila oogenesis.Fly (Austin). 2009 Jan-Mar;3(1):15-28. doi: 10.4161/fly.3.1.7751. Epub 2009 Jan 2. Fly (Austin). 2009. PMID: 19182536 Review.
-
[Mechanisms underlying maternal RNA translation and localization during Drosophila oogenesis].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009 Dec;54(16 Suppl):2159-64. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009. PMID: 21089634 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

