IKKɛ induces STING non-IFN immune responses via a mechanism analogous to TBK1
- PMID: 39262777
- PMCID: PMC11387596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110693
IKKɛ induces STING non-IFN immune responses via a mechanism analogous to TBK1
Abstract
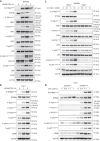
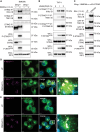
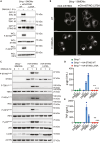
The cGAS-STING pathway responds to cytosolic DNA to elicit host immunity to infection. The activation of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) can trigger a number of critical cellular responses including inflammation, noncanonical autophagy, lipid metabolism, senescence, and cell death. STING-mediated immunity through the production of type I interferons (IFNs) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-driven proinflammatory cytokines is primarily driven via the effector protein TBK1. We have previously found that IκBα kinase epsilon (IKKε), a homolog of TBK1, can also facilitate STING-NF-κB responses. Therefore, a thorough understanding of how IKKε participates in STING signaling is essential. Here, we used a combination of genetic and biochemical approaches to provide mechanistic details into how IKKε confers non-IFN (e.g., NF-κB and MAPK) STING responses in macrophages, including in the absence of TBK1. We demonstrate a conserved mechanism of STING binding between TBK1 and IKKε. These findings strengthen our understanding of cGAS-STING signaling and the preservation of host immunity in cases of TBK1-deficiency.
Keywords: Cell biology; Immunology; Molecular biology.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TBK1 and IKKε Act Redundantly to Mediate STING-Induced NF-κB Responses in Myeloid Cells.Cell Rep. 2020 Apr 7;31(1):107492. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.056. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32268090
-
The Kinase MAP4K1 Inhibits Cytosolic RNA-Induced Antiviral Signaling by Promoting Proteasomal Degradation of TBK1/IKKε.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0145821. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01458-21. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34908452 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine IKKε is involved in the STING-induced type I IFN antiviral response of the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2023 Oct;299(10):105213. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105213. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37660925 Free PMC article.
-
The cGAS-STING signaling in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: Future novel target option for pharmacotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):50-75. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 May 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and spatial mechanisms governing STING signalling.FEBS J. 2021 Oct;288(19):5504-5529. doi: 10.1111/febs.15640. Epub 2020 Dec 11. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33237620 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

