A novel tumor-derived exosomal gene signature predicts prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 39262474
- PMCID: PMC11384923
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-23-2354
A novel tumor-derived exosomal gene signature predicts prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is a devastating disease with poor prognosis. Accumulating evidence has shown that exosomes and their cargo have the potential to mediate the progression of pancreatic cancer and are promising non-invasive biomarkers for the early detection and prognosis of this malignancy. This study aimed to construct a gene signature from tumor-derived exosomes with high prognostic capacity for pancreatic cancer using bioinformatics analysis.
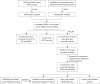
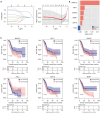
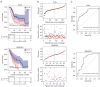
Methods: Gene expression data of solid pancreatic cancer tumors and blood-derived exosome tissues were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and ExoRBase 2.0. Overlapping differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the two datasets were analyzed, followed by functional enrichment analysis, protein-protein interaction networks, and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression of prognosis-related exosomal DEGs, a tumor-derived exosomal gene signature was constructed based on the TCGA dataset, which was validated by an external validation dataset, GSE62452. The prognostic power of this gene signature and its relationship with various pathways and immune cell infiltration were analyzed.
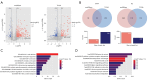
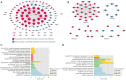
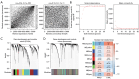
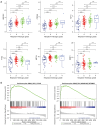
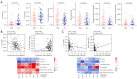
Results: A total of 166 overlapping DEGs were identified from the two datasets, which were markedly enriched in functions and pathways associated with the cell cycle. Two key modules and corresponding 70 exosomal DEGs were identified using WGCNA. Using LASSO Cox regression of prognosis-related exosomal DEGs, a tumor-derived exosomal gene signature was built using six exosomal DEGs (ARNTL2, FHL2, KRT19, MMP1, CDCA5, and KIF11), which showed high predictive performance for prognosis in both the training and validation datasets. In addition, this prognostic signature is associated with the differential activation of several pathways, such as the cell cycle, and the infiltration of some immune cells, such as Tregs and CD8+ T cells.
Conclusions: This study established a six-exosome gene signature that can accurately predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Pancreatic cancer; cell cycle; exosomes; gene signature; immune cell infiltration.
2024 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-23-2354/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a Nine-Gene Signature and Establishment of a Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Overall Survival of Pancreatic Cancer.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 27;9:996. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00996. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31612115 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a pyroptosis-related prognostic signature in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Apr 20;22(1):429. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09526-z. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35443644 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-cas9 Screening Identified Lethal Genes Enriched in Cell Cycle Pathway and of Prognosis Significance in Breast Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 19;9:646774. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646774. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33816496 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prognostic gene signature associated with microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2019 Nov 29;7:e8128. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8128. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31803536 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of an aging-related gene signature predicting the prognosis of pancreatic cancer.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 18;14:1022265. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1022265. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36741321 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
