MicroRNAs: pioneering regulators in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy
- PMID: 39256358
- PMCID: PMC11387755
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-03075-8
MicroRNAs: pioneering regulators in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy
Abstract
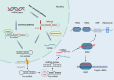
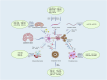
This article delves into Alzheimer's disease (AD), a prevalent neurodegenerative condition primarily affecting the elderly. It is characterized by progressive memory and cognitive impairments, severely disrupting daily life. Recent research highlights the potential involvement of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of AD. MicroRNAs (MiRNAs), short non-coding RNAs comprising 20-24 nucleotides, significantly influence gene regulation by hindering translation or promoting degradation of target genes. This review explores the role of specific miRNAs in AD progression, focusing on their impact on β-amyloid (Aβ) peptide accumulation, intracellular aggregation of hyperphosphorylated tau proteins, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and the expression of the APOE4 gene. Our insights contribute to understanding AD's pathology, offering new avenues for identifying diagnostic markers and developing novel therapeutic targets.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into the Role of microRNAs as Clinical Tools for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and as Therapeutic Targets in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 14;25(18):9936. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189936. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory roles of microRNAs in modulating mitochondrial dynamics, amyloid beta fibrillation, microglial activation, and cholinergic signaling: Implications for alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024 Jun;161:105685. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105685. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024. PMID: 38670299 Review.
-
Targeting Novel microRNAs in Developing Novel Alzheimer's Disease Treatments.Neurochem Res. 2023 Jan;48(1):26-38. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03734-6. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36048350 Review.
-
Abeta, tau and ApoE4 in Alzheimer's disease: the axonal connection.Trends Mol Med. 2007 Apr;13(4):135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2007.02.004. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Trends Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17344096
-
Cellular cholesterol homeostasis and Alzheimer's disease.J Lipid Res. 2017 Dec;58(12):2239-2254. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R075630. Epub 2017 Mar 15. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28298292 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Explorations of Neurological Disorders, the Identification Methods, and Therapeutic Avenues.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 30;25(21):11658. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111658. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82071676/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82071676/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82071676/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82071676/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

