Membrane properties and coupling of macroglia in the optic nerve
- PMID: 39253555
- PMCID: PMC11382002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crneur.2024.100137
Membrane properties and coupling of macroglia in the optic nerve
Abstract
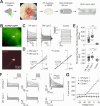
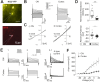
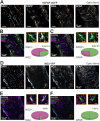
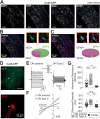
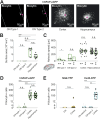
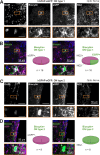
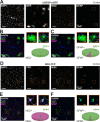
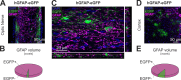
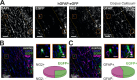
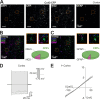
We established a longitudinal acute slice preparation of transgenic mouse optic nerve to characterize membrane properties and coupling of glial cells by patch-clamp and dye-filling, complemented by immunohistochemistry. Unlike in cortex or hippocampus, the majority of EGFP + cells in optic nerve of the hGFAP-EGFP transgenic mouse, a tool to identify astrocytes, were characterized by time and voltage dependent K+-currents including A-type K+-currents, properties previously described for NG2 glia. Indeed, the majority of transgene expressing cells in optic nerve were immunopositive for NG2 proteoglycan, whereas only a minority show GFAP immunoreactivity. Similar physiological properties were seen in YFP + cells from NG2-YFP transgenic mice, indicating that in optic nerve the transgene of hGFAP-EGFP animals is expressed by NG2 glia instead of astrocytes. Using Cx43kiECFP transgenic mice as another astrocyte-indicator revealed that astrocytes had passive membrane currents. Dye-filling showed that hGFAP-EGFP+ cells in optic nerve were coupled to none or few neighboring cells while hGFAP-EGFP+ cells in the cortex form large networks. Similarly, dye-filling of NG2-YFP+ and Cx43-CFP+ cells in optic nerve revealed small networks. Our work shows that identification of astrocytes in optic nerve requires distinct approaches, that the cells express membrane current patterns distinct from cortex and that they form small networks.
Keywords: Astrocyte; Cell coupling; In-situ patch clamp; Mouse optic nerve; NG2 glia; Transgenic reporter mouse.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity of Kir4.1 channel expression in glia revealed by mouse transgenesis.Glia. 2009 Dec;57(16):1706-15. doi: 10.1002/glia.20882. Glia. 2009. PMID: 19382212 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial organization of NG2 glial cells and astrocytes in rat hippocampal CA1 region.Hippocampus. 2014 Apr;24(4):383-95. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22232. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 24339242 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiologically "complex" glial cells freshly isolated from the hippocampus are immunopositive for the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan NG2.J Neurosci Res. 2003 Sep 15;73(6):765-77. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10680. J Neurosci Res. 2003. PMID: 12949902
-
Functions of optic nerve glia: axoglial signalling in physiology and pathology.Eye (Lond). 2004 Nov;18(11):1110-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6701595. Eye (Lond). 2004. PMID: 15534596 Review.
-
Morphological and physiological interactions of NG2-glia with astrocytes and neurons.J Anat. 2007 Jun;210(6):661-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00729.x. Epub 2007 Apr 25. J Anat. 2007. PMID: 17459143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

