The therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine in depression: focused on the modulation of neuroplasticity
- PMID: 39253375
- PMCID: PMC11381291
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1426769
The therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine in depression: focused on the modulation of neuroplasticity
Abstract
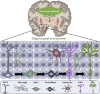
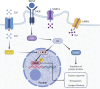
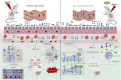
Depression, a mood disorder characterized by a persistent low mood and lack of enjoyment, is considered the leading cause of non-fatal health losses worldwide. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to adapt to external or internal stimuli, resulting in functional and structural changes. This process plays a crucial role in the development of depression. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) shows significant potential as a complementary and alternative therapy for neurological diseases, including depression. However, there has been no systematic summary of the role of neuroplasticity in the pathological development of depression and TCM Interventions currently. This review systematically summarized recent literature on changes in neuroplasticity in depression and analyzed the regulatory mechanisms of active metabolites in TCM and TCM formulas on neuroplasticity in antidepressant treatment. Additionally, this review discussed the limitations of current research and the application prospects of TCM in regulating neuroplasticity in antidepressant research.
Keywords: antidepressant; depression; major depressive disorder; neuroplasticity; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Lv, Yang, Lu, Zhang, Zhong, Cui, Huang, Teng and Sai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional Chinese medicine decoctions and Chinese patent medicines for the treatment of depression: Efficacies and mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 May 10;307:116272. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116272. Epub 2023 Feb 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36791924 Review.
-
Neuroplasticity: A Key Player in the Antidepressant Action of Chinese Herbal Medicine.Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(5):1115-1133. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X21500531. Epub 2021 May 27. Am J Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34049476 Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine in depression: Targeting adult hippocampal neurogenesis.Phytomedicine. 2022 Apr;98:153980. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153980. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35152089 Review.
-
From Perspective of Hippocampal Plasticity: Function of Antidepressant Chinese Medicine Xiaoyaosan.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Aug;30(8):747-758. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3908-0. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38900227 Review.
-
Neuroplasticity-related mechanisms underlying the antidepressant-like effects of traditional herbal medicines.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Oct;27(10):945-958. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28807619 Review.
References
-
- Aceto G., Colussi C., Leone L., Fusco S., Rinaudo M., Scala F., et al. (2020). Chronic mild stress alters synaptic plasticity in the nucleus accumbens through GSK3β-dependent modulation of Kv4.2 channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117 (14), 8143–8153. 10.1073/pnas.1917423117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- An J. H., Jang E. H., Kim A. Y., Fava M., Mischoulon D., Papakostas G. I., et al. (2019). Ratio of plasma BDNF to leptin levels are associated with treatment response in major depressive disorder but not in panic disorder: a 12-week follow-up study. J. Affect. Disord. 259, 349–354. 10.1016/j.jad.2019.08.021 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

