Renal tubular epithelial cell quality control mechanisms as therapeutic targets in renal fibrosis
- PMID: 39247486
- PMCID: PMC11377145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.01.001
Renal tubular epithelial cell quality control mechanisms as therapeutic targets in renal fibrosis
Abstract
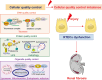
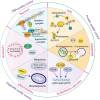
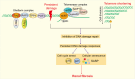
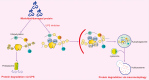
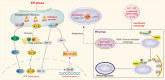
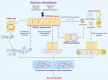
Renal fibrosis is a devastating consequence of progressive chronic kidney disease, representing a major public health challenge worldwide. The underlying mechanisms in the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis remain unclear, and effective treatments are still lacking. Renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs) maintain kidney function, and their dysfunction has emerged as a critical contributor to renal fibrosis. Cellular quality control comprises several components, including telomere homeostasis, ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), autophagy, mitochondrial homeostasis (mitophagy and mitochondrial metabolism), endoplasmic reticulum (ER, unfolded protein response), and lysosomes. Failures in the cellular quality control of RTECs, including DNA, protein, and organelle damage, exert profibrotic functions by leading to senescence, defective autophagy, ER stress, mitochondrial and lysosomal dysfunction, apoptosis, fibroblast activation, and immune cell recruitment. In this review, we summarize recent advances in understanding the role of quality control components and intercellular crosstalk networks in RTECs, within the context of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: Autophagy; Mitochondria; Quality control; Renal fibrosis; Renal tubular epithelial cells; Telomere homeostasis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathophysiological Role of Organelle Stress/Crosstalk in AKI-to-CKD Transition.Semin Nephrol. 2019 Nov;39(6):581-588. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2019.10.007. Semin Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31836040 Review.
-
Upregulation of TIPE1 in tubular epithelial cell aggravates diabetic nephropathy by disrupting PHB2 mediated mitophagy.Redox Biol. 2022 Apr;50:102260. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102260. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 35152003 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin alleviates kidney fibrosis by reducing renal tubular epithelial cell senescence through the SIRT1/PINK1/mitophagy axis.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 15;257:118116. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118116. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32702447
-
[Research Progress in Stress-Induced Senescence of Renal Tubular Cells in Diabetic Nephropathy].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Nov 20;54(6):1085-1090. doi: 10.12182/20231160107. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 38162078 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Organelle Stress and Crosstalk in Kidney Disease.Kidney360. 2020 Aug 7;1(10):1157-1164. doi: 10.34067/KID.0002442020. eCollection 2020 Oct 29. Kidney360. 2020. PMID: 35368784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yan H., Xu J., Xu Z., et al. Defining therapeutic targets for renal fibrosis: Exploiting the biology of pathogenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021;143 - PubMed
-
- Li L., Fu H., Liu Y. The fibrogenic niche in kidney fibrosis: Components and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022;18:545–557. - PubMed
-
- Pohl C., Dikic I. Cellular quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. Science. 2019;366:818–822. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

