Ultrasound super-resolution imaging for the assessment of renal allograft dysfunction: A pilot study
- PMID: 39247269
- PMCID: PMC11380004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36515
Ultrasound super-resolution imaging for the assessment of renal allograft dysfunction: A pilot study
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to examine the feasibility and practical application of ultrasound (US) super-resolution imaging (SRI) in evaluating microvasculature and measuring renal allograft function.
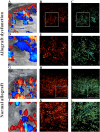
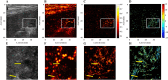
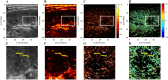
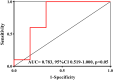
Methods: Sixteen consecutive patients who received kidney transplants were prospectively enrolled. The patients were assigned as: normal allograft function (n = 6), and allograft malfunction (n = 10). Localizing each potential contrast signal resulted in super-resolution images (SRI). SRI was utilized to assess micro-vessel density (MVD) and microvascular flow rate, whereas contrast-enhanced (CE) US images were statistically processed to get the time to peak (TTP) and peak intensity. Logistic regression was utilized to evaluate their relationship.
Results: US SRI may be utilized effectively on allografts to show microvasculature with significantly higher resolution than typical color Doppler flow and CEUS pictures. In the multivariate analysis, MVD and TTP were significant US markers of renal allograft failure (p = 0.031 and p = 0.045). The combination of MVD and TTP produced an AUC of 0.783 (p < 0.05) for allograft dysfunction.
Conclusions: SRI can accurately portray the microvasculature of renal allografts, while MVD and TTP are appropriate US markers for assessing renal allograft failure.
Keywords: Kidney transplantation; Renal allograft dysfunction; Super-resolution imaging; Ultrasound.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound super-resolution imaging for differential diagnosis of breast masses.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 3;12:1049991. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1049991. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36408165 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound super-resolution imaging for the differential diagnosis of thyroid nodules: A pilot study.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 27;12:978164. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.978164. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387122 Free PMC article.
-
Value of Ultrasound Super-Resolution Imaging for the Assessment of Renal Microcirculation in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Preliminary Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;14(11):1192. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14111192. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893718 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Clinical Applications for Super-resolution Ultrasound Localization Microscopy.Curr Med Sci. 2022 Feb;42(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s11596-021-2459-2. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Curr Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35167000 Review.
-
The Usefulness of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in the Assessment of Early Kidney Transplant Function and Complications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2017 Sep 15;7(3):53. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics7030053. Diagnostics (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28914777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

