Human coronaviruses activate and hijack the host transcription factor HSF1 to enhance viral replication
- PMID: 39243335
- PMCID: PMC11380654
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05370-5
Human coronaviruses activate and hijack the host transcription factor HSF1 to enhance viral replication
Abstract
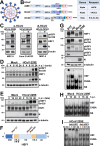
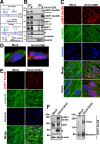
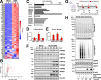
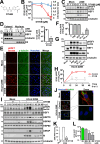
Organisms respond to proteotoxic-stress by activating the heat-shock response, a cellular defense mechanism regulated by a family of heat-shock factors (HSFs); among six human HSFs, HSF1 acts as a proteostasis guardian regulating severe stress-driven transcriptional responses. Herein we show that human coronaviruses (HCoV), both low-pathogenic seasonal-HCoVs and highly-pathogenic SARS-CoV-2 variants, are potent inducers of HSF1, promoting HSF1 serine-326 phosphorylation and triggering a powerful and distinct HSF1-driven transcriptional-translational response in infected cells. Despite the coronavirus-mediated shut-down of the host translational machinery, selected HSF1-target gene products, including HSP70, HSPA6 and AIRAP, are highly expressed in HCoV-infected cells. Using silencing experiments and a direct HSF1 small-molecule inhibitor we show that, intriguingly, HCoV-mediated activation of the HSF1-pathway, rather than representing a host defense response to infection, is hijacked by the pathogen and is essential for efficient progeny particles production. The results open new scenarios for the search of innovative antiviral strategies against coronavirus infections.
Keywords: HCoV-229E; HCoV-NL63; HCoV-OC43; Heat shock response; Protein homeostasis; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Seasonal human coronaviruses OC43, 229E, and NL63 induce cell surface modulation of entry receptors and display host cell-specific viral replication kinetics.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0422023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04220-23. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38864599 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of STING Signaling Pathway Effectively Blocks Human Coronavirus Infection.J Virol. 2021 May 24;95(12):e00490-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00490-21. Print 2021 May 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33789998 Free PMC article.
-
An overview on the seven pathogenic human coronaviruses.Rev Med Virol. 2022 Mar;32(2):e2282. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2282. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Rev Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34339073 Review.
-
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Vaccination Boosts Neutralizing Activity Against Seasonal Human Coronaviruses.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e653-e661. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac057. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35079775 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary trajectory of SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants.Virol J. 2021 Aug 13;18(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01633-w. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34389034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N 2010PHT9NF-006/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PE00000007/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca
- INF-ACT/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca
- UK/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U105181010/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

