Heat shock proteins as hallmarks of cancer: insights from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 39232809
- PMCID: PMC11375894
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-024-01601-1
Heat shock proteins as hallmarks of cancer: insights from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
Abstract
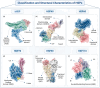
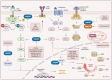
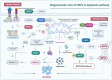
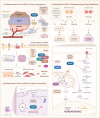
Heat shock proteins are essential molecular chaperones that play crucial roles in stabilizing protein structures, facilitating the repair or degradation of damaged proteins, and maintaining proteostasis and cellular functions. Extensive research has demonstrated that heat shock proteins are highly expressed in cancers and closely associated with tumorigenesis and progression. The "Hallmarks of Cancer" are the core features of cancer biology that collectively define a series of functional characteristics acquired by cells as they transition from a normal state to a state of tumor growth, including sustained proliferative signaling, evasion of growth suppressors, resistance to cell death, enabled replicative immortality, the induction of angiogenesis, and the activation of invasion and metastasis. The pivotal roles of heat shock proteins in modulating the hallmarks of cancer through the activation or inhibition of various signaling pathways has been well documented. Therefore, this review provides an overview of the roles of heat shock proteins in vital biological processes from the perspective of the hallmarks of cancer and summarizes the small-molecule inhibitors that target heat shock proteins to regulate various cancer hallmarks. Moreover, we further discuss combination therapy strategies involving heat shock proteins and promising dual-target inhibitors to highlight the potential of targeting heat shock proteins for cancer treatment. In summary, this review highlights how targeting heat shock proteins could regulate the hallmarks of cancer, which will provide valuable information to better elucidate and understand the roles of heat shock proteins in oncology and the mechanisms of cancer occurrence and development and aid in the development of more efficacious and less toxic novel anticancer agents.
Keywords: Cancer; Combination strategy; Dual inhibitors; Hallmarks of cancer; Heat shock protein; Target therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chaperoning the Cancer: The Proteostatic Functions of the Heat Shock Proteins in Cancer.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2017;12(1):35-47. doi: 10.2174/1574892811666161102125252. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 27809750 Review.
-
The therapeutic target Hsp90 and cancer hallmarks.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(3):347-65. doi: 10.2174/138161213804143725. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 22920906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the dual functional effects of heat shock proteins (HSPs) in cancer hallmarks to aid development of HSP inhibitors.Genome Med. 2020 Nov 23;12(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00795-6. Genome Med. 2020. PMID: 33225964 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock proteins in cancer: targeting the 'chaperones'.Future Med Chem. 2012 May;4(7):927-35. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.50. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22571616 Review.
-
Targeting Heat Shock Proteins in Cancer: A Promising Therapeutic Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 15;18(9):1978. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091978. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28914774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

