The role of RNA modifications in hepatocellular carcinoma: functional mechanism and potential applications
- PMID: 39229278
- PMCID: PMC11368726
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1439485
The role of RNA modifications in hepatocellular carcinoma: functional mechanism and potential applications
Abstract
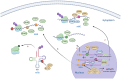
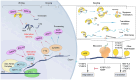
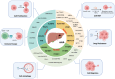
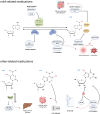
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly aggressive cancer with a poor prognosis. The molecular mechanisms underlying its development remain unclear. Recent studies have highlighted the crucial role of RNA modifications in HCC progression, which indicates their potential as therapeutic targets and biomarkers for managing HCC. In this review, we discuss the functional role and molecular mechanisms of RNA modifications in HCC through a review and summary of relevant literature, to explore the potential therapeutic agents and biomarkers for diagnostic and prognostic of HCC. This review indicates that specific RNA modification pathways, such as N6-methyladenosine, 5-methylcytosine, N7-methylguanosine, and N1-methyladenosine, are erroneously regulated and are involved in the proliferation, autophagy, innate immunity, invasion, metastasis, immune cell infiltration, and drug resistance of HCC. These findings provide a new perspective for understanding the molecular mechanisms of HCC, as well as potential targets for the diagnosis and treatment of HCC by targeting specific RNA-modifying enzymes or recognition proteins. More than ten RNA-modifying regulators showed the potential for use for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment decision utility biomarkers of HCC. Their application value for HCC biomarkers necessitates extensive multi-center sample validation in the future. A growing number of RNA modifier inhibitors are being developed, but the lack of preclinical experiments and clinical studies targeting RNA modification in HCC poses a significant obstacle, and further research is needed to evaluate their application value in HCC treatment. In conclusion, this review provides an in-depth understanding of the complex interplay between RNA modifications and HCC while emphasizing the promising potential of RNA modifications as therapeutic targets and biomarkers for managing HCC.
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine; N1-methyladenosine; N6-methyladenosine; N7-methylguanosine; biomarkers; hepatocellular carcinoma; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Zhang, Xu and Hao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression pattern and prognostic value of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation key regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mutagenesis. 2021 Oct 6;36(5):369-379. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geab032. Mutagenesis. 2021. PMID: 34467992 Free PMC article.
-
The role of RNA modification in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 2;13:984453. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984453. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m1A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns correlated with autophagy to predict the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 22;24(1):506. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12235-4. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38649860 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine with immune infiltration and PD-L1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: novel perspective to personalized diagnosis and treatment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 3;14:1153802. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1153802. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37469973 Free PMC article.
-
New horizons for the role of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in hepatocellular carcinoma.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Jun;45(6):1130-1141. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01214-3. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38195693 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

