This is a preprint.
Transmembrane channel-like 4 and 5 proteins at microvillar tips are potential ion channels and lipid scramblases
- PMID: 39229161
- PMCID: PMC11370596
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.08.22.609173
Transmembrane channel-like 4 and 5 proteins at microvillar tips are potential ion channels and lipid scramblases
Abstract
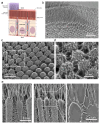
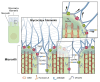
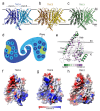
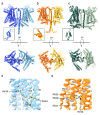
Microvilli-membrane bound actin protrusions on the surface of epithelial cells-are sites of critical processes including absorption, secretion, and adhesion. Increasing evidence suggests microvilli are mechanosensitive, but underlying molecules and mechanisms remain unknown. Here, we localize transmembrane channel-like proteins 4 and 5 (TMC4 and 5) and calcium and integrin binding protein 3 (CIB3) to microvillar tips in intestinal epithelial cells, near glycocalyx insertion sites. We find that TMC5 colocalizes with CIB3 in cultured cells and that a TMC5 fragment forms a complex with CIB3 in vitro. Homology and AlphaFold2 models reveal a putative ion permeation pathway in TMC4 and 5, and molecular dynamics simulations predict both proteins can conduct ions and perform lipid scrambling. These findings raise the possibility that TMC4 and 5 interact with CIB3 at microvillar tips to form a mechanosensitive complex, akin to TMC1 and 2, and CIB2 and 3, within the mechanotransduction channel complex at the tips of inner ear stereocilia.
Figures
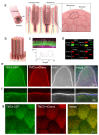
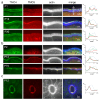
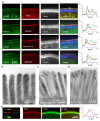
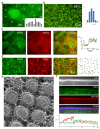
Similar articles
-
Complexes of vertebrate TMC1/2 and CIB2/3 proteins form hair-cell mechanotransduction cation channels.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 5:2023.05.26.542533. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.26.542533. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2025 Jan 08;12:RP89719. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89719 PMID: 37398045 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CIB2 and CIB3 are auxiliary subunits of the mechanotransduction channel of hair cells.Neuron. 2021 Jul 7;109(13):2131-2149.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.05.007. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 34089643 Free PMC article.
-
TMC1 and TMC2 Localize at the Site of Mechanotransduction in Mammalian Inner Ear Hair Cell Stereocilia.Cell Rep. 2015 Sep 8;12(10):1606-17. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.058. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26321635 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanically Gated Ion Channels in Mammalian Hair Cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Apr 11;12:100. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00100. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29755320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and Dysfunction of TMC Channels in Inner Ear Hair Cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019 Oct 1;9(10):a033506. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033506. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019. PMID: 30291150 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Delacour D., Salomon J., Robine S. & Louvard D. Plasticity of the brush border — the yin and yang of intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 13, 161–174 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Müller T. et al. MYO5B mutations cause microvillus inclusion disease and disrupt epithelial cell polarity. Nat. Genet. 40, 1163–1165 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Ruemmele F. M. et al. Loss-of-function of MYO5B is the main cause of microvillus inclusion disease: 15 novel mutations and a CaCo-2 RNAicell model. Hum. Mutat. 31, 544–551 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
