Astaxanthin activated the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway to inhibit ferroptosis and enhance autophagy, ameliorating dry eye disease
- PMID: 39224780
- PMCID: PMC11366873
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1407659
Astaxanthin activated the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway to inhibit ferroptosis and enhance autophagy, ameliorating dry eye disease
Abstract
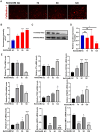
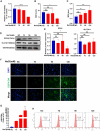
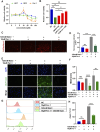
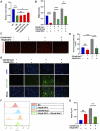
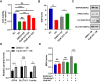
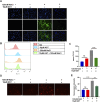
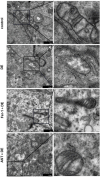
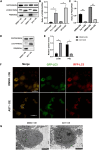
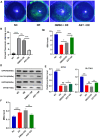
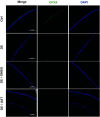
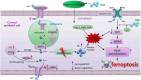
Dry eye disease (DED) is a common eye disease in clinical practice. The crucial pathogenesis of DED is that hyperosmolarity activates oxidative stress signaling pathways in corneal epithelial and immune cells and, thus, produces inflammatory molecules. The complex pathological changes in the dry eye still need to be elucidated to facilitate treatment. In this study, we found that astaxanthin (AST) can protect against DED through the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. After treatment with AST, the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway was positively activated in DED both in vivo and in vitro, accompanied by enhanced autophagy and decreased ferroptosis. In hyperosmolarity-induced DED corneal epithelial cells, AST increased the expression of ferritin to promote iron storage and reduce Fe2+ overload. It increased glutathione (GSH) and GPX4, scavenged reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxide, and rescued the mitochondrial structure to prevent ferroptosis. Furthermore, inhibition of ferroptosis by ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1), iron chelator deferoxamine mesylate (DFO), or AST could activate healthy autophagic flux. In addition, in a dry eye mouse model, AST upregulated SLC7A11 and GPX4 and inhibited ferroptosis. To summarize, we found that AST can ameliorate DED by reinforcing the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway, which mainly affects oxidative stress, autophagy, and ferroptosis processes.
Keywords: astaxanthin; autophagy; corneal epithelial; dry eye; ferroptosis.
Copyright © 2024 Hou, Xiao, Wang, Pan, Liu, Lu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of SLC7A11-GPX4 signal pathway is involved in aconitine-induced ferroptosis in vivo and in vitro.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:116029. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116029. Epub 2022 Dec 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36503029
-
Lipid Peroxidation, GSH Depletion, and SLC7A11 Inhibition Are Common Causes of EMT and Ferroptosis in A549 Cells, but Different in Specific Mechanisms.DNA Cell Biol. 2021 Feb;40(2):172-183. doi: 10.1089/dna.2020.5730. Epub 2020 Dec 22. DNA Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33351681
-
Ferrostatin-1 inhibits ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells and alleviates abdominal aortic aneurysm formation through activating the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis.FASEB J. 2024 Jan 31;38(2):e23401. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300198RRR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38236196
-
Astragaloside IV regulates the ferroptosis signaling pathway via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis to inhibit PM2.5-mediated lung injury in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109186. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109186. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36115280 Review.
-
Lipid Peroxidation and Iron Metabolism: Two Corner Stones in the Homeostasis Control of Ferroptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 27;24(1):449. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010449. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

