Posttransplant complications: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 39224537
- PMCID: PMC11366828
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.669
Posttransplant complications: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
Abstract
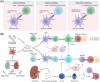
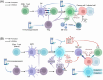
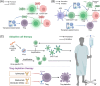
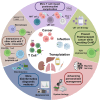
Posttransplantation complications pose a major challenge to the long-term survival and quality of life of organ transplant recipients. These complications encompass immune-mediated complications, infectious complications, metabolic complications, and malignancies, with each type influenced by various risk factors and pathological mechanisms. The molecular mechanisms underlying posttransplantation complications involve a complex interplay of immunological, metabolic, and oncogenic processes, including innate and adaptive immune activation, immunosuppressant side effects, and viral reactivation. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of the clinical features, risk factors, and molecular mechanisms of major posttransplantation complications. We systematically summarize the current understanding of the immunological basis of allograft rejection and graft-versus-host disease, the metabolic dysregulation associated with immunosuppressive agents, and the role of oncogenic viruses in posttransplantation malignancies. Furthermore, we discuss potential prevention and intervention strategies based on these mechanistic insights, highlighting the importance of optimizing immunosuppressive regimens, enhancing infection prophylaxis, and implementing targeted therapies. We also emphasize the need for future research to develop individualized complication control strategies under the guidance of precision medicine, ultimately improving the prognosis and quality of life of transplant recipients.
Keywords: T cell; infection; malignancy; organ transplantation; posttransplant complications; rejection.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Malignancy after Solid Organ Transplantation: Comprehensive Imaging Review.Radiographics. 2016 Sep-Oct;36(5):1390-407. doi: 10.1148/rg.2016150175. Radiographics. 2016. PMID: 27618321 Review.
-
Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Consult Series #66: Prepregnancy evaluation and pregnancy management of patients with solid organ transplants.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Aug;229(2):B10-B32. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.04.022. Epub 2023 Apr 22. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 37088276 Review.
-
Treatment strategies to minimize or prevent chronic allograft dysfunction in pediatric renal transplant recipients: an overview.Paediatr Drugs. 2009;11(6):381-96. doi: 10.2165/11316100-000000000-00000. Paediatr Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19877724 Review.
-
Metabolic Complications in Liver Transplantation Recipients: How We Can Optimize Long-Term Survival.Liver Transpl. 2021 Oct;27(10):1468-1478. doi: 10.1002/lt.26219. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Liver Transpl. 2021. PMID: 34165872 Review.
-
CCL8 and the Immune Control of Cytomegalovirus in Organ Transplant Recipients.Am J Transplant. 2015 Jul;15(7):1882-92. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13207. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Am J Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25764912
References
-
- Datta RR, Schran S, Persa OD, et al. Post‐transplant malignancies show reduced T‐cell abundance and tertiary lymphoid structures as correlates of impaired cancer immunosurveillance. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(8):1712‐1723. - PubMed
-
- Conrad SA, Chhabra A, Vay D. Long‐term follow‐up and complications after cardiac transplantation. J La State Med Soc. 1993;145(5):217‐220. 223–5. - PubMed
-
- Sen A, Callisen H, Libricz S, Patel B. Complications of solid organ transplantation: cardiovascular, neurologic, renal, and gastrointestinal. Crit Care Clin. 2019;35(1):169‐186. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
