Tyrosine kinases: multifaceted receptors at the intersection of several neurodegenerative disease-associated processes
- PMID: 39221072
- PMCID: PMC11361951
- DOI: 10.3389/frdem.2024.1458038
Tyrosine kinases: multifaceted receptors at the intersection of several neurodegenerative disease-associated processes
Abstract
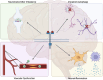
Tyrosine kinases (TKs) are catalytic enzymes activated by auto-phosphorylation that function by phosphorylating tyrosine residues on downstream substrates. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been heavily exploited as cancer therapeutics, primarily due to their role in autophagy, blood vessel remodeling and inflammation. This suggests tyrosine kinase inhibition as an appealing therapeutic target for exploiting convergent mechanisms across several neurodegenerative disease (NDD) pathologies. The overlapping mechanisms of action between neurodegeneration and cancer suggest that TKIs may play a pivotal role in attenuating neurodegenerative processes, including degradation of misfolded or toxic proteins, reduction of inflammation and prevention of fibrotic events of blood vessels in the brain. In this review, we will discuss the distinct roles that select TKs have been shown to play in various disease-associated processes, as well as identify TKs that have been explored as targets for therapeutic intervention and associated pharmacological agents being investigated as treatments for NDDs.
Keywords: autophagy; blood vessels; c-KIT; inflammation; neurodegenerative diseases; tyrosine kinase.
Copyright © 2024 Stevenson, Algarzae and Moussa.
Conflict of interest statement
CM is an inventor on several US and international Georgetown University patents to use BK40143 and BK40197 and other tyrosine kinase inhibitors as a treatment for neurodegenerative diseases. Georgetown University spun out the technology (April 2020) to a start-up company, KeifeRx, in which it holds equity and for which CM is a co-founder, shareholder, and consultant. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging roles of tyrosine kinases in hepatic inflammatory diseases and therapeutic opportunities.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jul;120:110373. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110373. Epub 2023 May 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37257270 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors (EGFRIs) and their Role in the Treatment of Cancer: A Review.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(20):3370-3381. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220408090541. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35400324 Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Sep;5(5):390-401. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelets and tyrosine kinase inhibitors: clinical features, mechanisms of action, and effects on physiology.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):C1231-C1250. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00040.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35938677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From discovery of tyrosine phosphorylation to targeted cancer therapies: The 2018 Tang Prize in Biopharmaceutical Science.Biomed J. 2019 Apr;42(2):80-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Biomed J. 2019. PMID: 31130251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arsenault S., Benoit R. Y., Clift F., Moore C. S. (2022). Does the use of the Bruton Tyrosine Kinase inhibitors and the c-kit inhibitor masitinib result in clinically significant outcomes among patients with various forms of multiple sclerosis? Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 67:104164. 10.1016/j.msard.2022.104164 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

