Harnessing IL-2 for immunotherapy against cancer and chronic infection: a historical perspective and emerging trends
- PMID: 39218982
- PMCID: PMC11447265
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01301-3
Harnessing IL-2 for immunotherapy against cancer and chronic infection: a historical perspective and emerging trends
Abstract
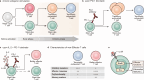
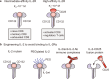
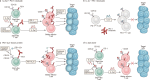
IL-2 therapy, which enhances the function of CD8 + T cells, was initially employed as the cornerstone of immunotherapy against cancer. However, the impact of this therapy extends beyond CD8 + T cells to cells expressing IL-2R, such as endothelial cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs), resulting in various side effects. Consequently, IL-2 therapy has taken a step back from the forefront of treatment. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies and CTLA-4 antibodies, are used because of their durable therapeutic responses and the reduced incidence of side effects. Nevertheless, only a small fraction of cancer patients respond to ICIs, and research on IL-2 as a combination treatment to improve the efficacy of these ICIs is ongoing. To mitigate side effects, efforts have focused on developing IL-2 variants that do not strongly bind to cells expressing IL-2Rα and favor signaling through IL-2Rβγ. However, recent studies have suggested that, in the context of persistent antigen stimulation models, effective stimulation of antigen-specific exhausted CD8 + T cells in combination with PD-1 inhibitors requires either 1) binding to IL-2Rα or 2) delivery via a fusion with PD-1. This review explores the historical context of IL-2 as an immunotherapeutic agent and discusses future directions for its use in cancer immunotherapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory Precision: A Narrative Review Exploring the Critical Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 17;25(10):5490. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105490. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors: breakthroughs in cancer treatment.Cancer Biol Med. 2024 May 24;21(6):451-72. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0055. Cancer Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38801082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Combination of Anti-PD-L1 Treatment and Therapeutic Vaccination Facilitates Improved Retroviral Clearance via Reactivation of Highly Exhausted T Cells.mBio. 2021 Feb 2;12(1):e02121-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02121-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33531395 Free PMC article.
-
MB2033, an anti-PD-L1 × IL-2 variant fusion protein, demonstrates robust anti-tumor efficacy with minimal peripheral toxicity.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Jun 4;73(8):157. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03742-1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38834889 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and development of ANV419, an IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody fusion protein with potent CD8+ T and natural killer cell-stimulating capacity for cancer immunotherapy.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2381891. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2381891. Epub 2024 Jul 23. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39041287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spolski, R., Li, P. & Leonard, W. J. Biology and regulation of IL-2: from molecular mechanisms to human therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol.18, 648–659 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Gaffen, S. L. & Liu, K. D. Overview of interleukin-2 function, production and clinical applications. Cytokine28, 109–123 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Hernandez, R., Poder, J., LaPorte, K. M. & Malek, T. R. Engineering IL-2 for immunotherapy of autoimmunity and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol.22, 614–628 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Mullard, A. Restoring IL-2 to its cancer immunotherapy glory. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.20, 163–165 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

