Past trends and future projections of palliative care needs in Chile: analysis of routinely available death registry and population data
- PMID: 39218926
- PMCID: PMC11367822
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03570-1
Past trends and future projections of palliative care needs in Chile: analysis of routinely available death registry and population data
Abstract
Background: The number of people with palliative care needs is projected to increase globally. Chile has recently introduced legislation for universal access to palliative care services for patients with severe and terminal illnesses, including non-cancer conditions. We aimed to estimate the number of people affected by serious health-related suffering and need for palliative care in Chile to 2050.
Methods: We used data on all deaths registered in Chile between 1997-2019 and population estimates for 1997-2050. We used Poisson regression to model past trends in causes of death adjusted by age, sex and population estimates, to project the number of deaths for each cause from 2021 to 2050. We applied the Lancet Commission on Palliative Care and Pain Relief weights to these projections to identify decedents and non-decedents with palliative care needs.
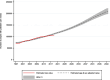
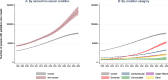
Results: Population palliative care needs in Chile are projected to increase from 117 (95% CI 114 to 120) thousand people in 2021 to 209 (95% CI 198 to 223) thousand people in 2050, a 79% increase (IRR 1.79; 95% CI 1.78-1.80). This increase will be driven by non-cancer conditions, particularly dementia (IRR 2.9, 95% CI 2.85-2.95) and cardiovascular conditions (IRR 1.86, 95% CI 1.83-1.89). By 2050, 50% of those estimated to need palliative care will be non-decedents (not expected to die within a year).
Conclusions: Chile will experience a large increase in palliative care needs, particularly for people with dementia and other non-cancer conditions. Improved availability of high-quality services, expanded clinician training and new sustainable models of care are urgently required to ensure universal access to palliative care.
Keywords: Palliative care needs; Population estimations; Projections; Serious health-related suffering.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Undernutrition as a risk factor for tuberculosis disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 11;6(6):CD015890. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015890.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38860538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous