Metabolomics and Lipidomics for Studying Metabolic Syndrome: Insights into Cardiovascular Diseases, Type 1 & 2 Diabetes, and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
- PMID: 39212142
- PMCID: PMC11412346
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.935443
Metabolomics and Lipidomics for Studying Metabolic Syndrome: Insights into Cardiovascular Diseases, Type 1 & 2 Diabetes, and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Abstract
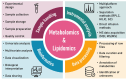
Metabolomics and lipidomics have emerged as tools in understanding the connections of metabolic syndrome (MetS) with cardiovascular diseases (CVD), type 1 and type 2 diabetes (T1D, T2D), and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). This review highlights the applications of these omics approaches in large-scale cohort studies, emphasizing their role in biomarker discovery and disease prediction. Integrating metabolomics and lipidomics has significantly advanced our understanding of MetS pathology by identifying unique metabolic signatures associated with disease progression. However, challenges such as standardizing analytical workflows, data interpretation, and biomarker validation remain critical for translating research findings into clinical practice. Future research should focus on optimizing these methodologies to enhance their clinical utility and address the global burden of MetS-related diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathophysiological Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 10;25(16):8731. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168731. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking of metabolomic biomarkers with cardiometabolic health in Chinese population.J Diabetes. 2019 Apr;11(4):280-291. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12858. Epub 2018 Oct 30. J Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 30239137 Review.
-
Omics-based biomarkers as useful tools in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease clinical practice: How far are we?World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr 14;30(14):1982-1989. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1982. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38681130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of metabolite profiles of metabolic syndrome using untargeted and targeted LC-MS based lipidomics approach.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Jan 5;177:112848. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112848. Epub 2019 Aug 29. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 31479998
-
Integrative Lipidomics and Metabolomics for System-Level Understanding of the Metabolic Syndrome in Long-Term Treated HIV-Infected Individuals.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 12;12:742736. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.742736. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart JC, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–1645. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Han TS, Lean MEJ. Metabolic syndrome. Medicine. 2015;43:80–87. doi: 10.1016/j.mpmed.2014.11.006. - DOI
