Notch Signaling Suppression by Golden Phytochemicals: Potential for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 39206407
- PMCID: PMC11347744
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2024.035
Notch Signaling Suppression by Golden Phytochemicals: Potential for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
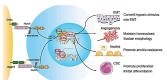
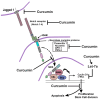
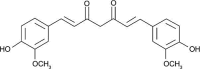
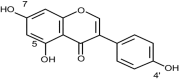
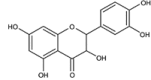
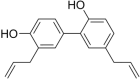
Cancer is one of the main causes of mortality worldwide. Cancer cells are characterized by unregulated cellular processes, including proliferation, progression, and angiogenesis. The occurrence of these processes is due to the dysregulation of various signaling pathways such as NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB), Wnt/beta-catenin, Notch signaling and MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinases). Notch signaling pathways cause the progression of various types of malignant tumors. Among the phytochemicals for cancer therapy, several have attracted great interest, including curcumin, genistein, quercetin, silibinin, resveratrol, cucurbitacin and glycyrrhizin. Given the great cellular and molecular heterogeneity within tumors and the high toxicity and side effects of synthetic chemotherapeutics, natural products with pleiotropic effects that simultaneously target numerous signaling pathways appear to be ideal substitutes for cancer therapy. With this in mind, we take a look at the current status, impact and potential of known compounds as golden phytochemicals on key signaling pathways in tumors, focusing on the Notch pathway. This review may be useful for discovering new molecular targets for safe and efficient cancer therapy with natural chemotherapeutics.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell signaling; Natural compounds; Notch signaling pathway; Phytochemicals.
©2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Targeting Major Signaling Pathways of Bladder Cancer with Phytochemicals: A Review.Nutr Cancer. 2021;73(11-12):2249-2271. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1856895. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Nutr Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33305598 Review.
-
Regulation of the Notch signaling pathway by natural products for cancer therapy.J Nutr Biochem. 2024 Jan;123:109483. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109483. Epub 2023 Oct 15. J Nutr Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37848105 Review.
-
Genistein and cancer: current status, challenges, and future directions.Adv Nutr. 2015 Jul 15;6(4):408-19. doi: 10.3945/an.114.008052. Print 2015 Jul. Adv Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26178025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting cancer stem cells and signalling pathways through phytochemicals: A promising approach against colorectal cancer.Phytomedicine. 2023 Jan;108:154524. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154524. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36375238 Review.
-
Dietary Phytochemicals in Cancer Signalling Pathways: Role of miRNA Targeting.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(39):8036-8067. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210420101605. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33881968 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources