Binding to the Other Side: The AT-Hook DNA-Binding Domain Allows Nuclear Factors to Exploit the DNA Minor Groove
- PMID: 39201549
- PMCID: PMC11354804
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168863
Binding to the Other Side: The AT-Hook DNA-Binding Domain Allows Nuclear Factors to Exploit the DNA Minor Groove
Abstract
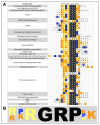
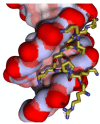
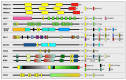
The "AT-hook" is a peculiar DNA-binding domain that interacts with DNA in the minor groove in correspondence to AT-rich sequences. This domain has been first described in the HMGA protein family of architectural factors and later in various transcription factors and chromatin proteins, often in association with major groove DNA-binding domains. In this review, using a literature search, we identified about one hundred AT-hook-containing proteins, mainly chromatin proteins and transcription factors. After considering the prototypes of AT-hook-containing proteins, the HMGA family, we review those that have been studied in more detail and that have been involved in various pathologies with a particular focus on cancer. This review shows that the AT-hook is a domain that gives proteins not only the ability to interact with DNA but also with RNA and proteins. This domain can have enzymatic activity and can influence the activity of the major groove DNA-binding domain and chromatin docking modules when present, and its activity can be modulated by post-translational modifications. Future research on the function of AT-hook-containing proteins will allow us to better decipher their function and contribution to the different pathologies and to eventually uncover their mutual influences.
Keywords: AKNA; AT-hook; BRG1; EBNA1; HMGA; LEDGF/p75; MLL1; MeCP2; PATZ1; ZFAT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the HMGA AT-hook 1 domain bound to the minor groove of AT-rich DNA and inhibition by antikinetoplastid drugs.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 30;14(1):26173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77522-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39478017 Free PMC article.
-
A tripartite DNA-binding element, comprised of the nuclear localization signal and two AT-hook motifs, mediates the association of LEDGF/p75 with chromatin in vivo.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Mar 20;34(5):1653-65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl052. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16549878 Free PMC article.
-
The extended AT-hook is a novel RNA binding motif.RNA Biol. 2015;12(8):864-76. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1060394. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26156556 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin-associated HMGA and HMGB proteins: versatile co-regulators of DNA-dependent processes.Plant Mol Biol. 2003 Oct;53(3):281-95. doi: 10.1023/b:plan.0000007002.99408.ba. Plant Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14750519 Review.
-
Molecular biology of HMGA proteins: hubs of nuclear function.Gene. 2001 Oct 17;277(1-2):63-81. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00689-8. Gene. 2001. PMID: 11602345 Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of the HMGA AT-hook 1 domain bound to the minor groove of AT-rich DNA and inhibition by antikinetoplastid drugs.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 30;14(1):26173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77522-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39478017 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

