Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Ombuin from Rhamnus erythroxylon Pall. Leaves in LPS-Induced BV-2 Microglia by Targeting Src and Suppressing the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 39201475
- PMCID: PMC11354356
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168789
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Ombuin from Rhamnus erythroxylon Pall. Leaves in LPS-Induced BV-2 Microglia by Targeting Src and Suppressing the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
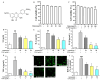
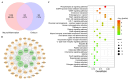
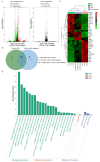
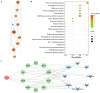
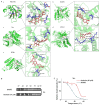
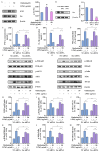
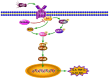
The leaves of Rhamnus erythroxylon Pall. are widely used as tea substitutes in northwest China for their fragrant aroma, anti-irritability, and digestion-enhancing properties. Ombuin, a main flavonoid compound found in the leaves, exhibited notable anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. However, its potential role in treating neuroinflammatory-related diseases remains unexplored. Thus, this study aims to evaluate the anti-neuroinflammatory effects of ombuin and to explore the underlying molecular mechanisms. According to our findings, ombuin dramatically reduced the release of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1β, nitric oxide (NO), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV-2 microglia. Further analysis, including transcriptomics, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and cellular heat transfer assays, revealed that Src was a direct target of ombuin. Western blot analysis showed that ombuin effectively suppressed Src phosphorylation and inhibited the downstream expressions of p-PI3K p85, p-AKT1, p-IKKα/β, p-IκBα, and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). Meanwhile, the repression of Src significantly reversed the anti-neuroinflammatory activity of ombuin. Our results identified Src as a direct target of ombuin and implied that ombuin exerted an anti-neuroinflammatory effect by inhibiting Src phosphorylation and suppressing the activation of the PI3K-AKT and NF-κB pathways, which might provide an alternative therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: BV-2; LPS; Src; neuroinflammation; ombuin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2012 Jan;12(1):278-87. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.12.001. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22193240
-
Isobutyrylshikonin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in BV2 microglial cells by suppressing the PI3K/Akt-mediated nuclear transcription factor-κB pathway.Nutr Res. 2014 Dec;34(12):1111-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Nutr Res. 2014. PMID: 25454762
-
Potential chemoprevention of LPS-stimulated nitric oxide and prostaglandin E₂ production by α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-3-indolecarbonate in BV2 microglial cells through suppression of the ROS/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway.Neurochem Int. 2014 Feb;67:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24486459
-
Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells.Immunobiology. 2013 Dec;218(12):1452-67. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 9. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23735482
-
Oroxylin A: A Promising Flavonoid for Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 26;12(9):1185. doi: 10.3390/biom12091185. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Decandia D., Gelfo F., Landolfo E., Balsamo F., Petrosini L., Cutuli D. Dietary Protection against Cognitive Impairment, Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease Animal Models of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:5921. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065921. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

