Virtual Screening and Validation of Affinity DNA Functional Ligands for IgG Fc Segment
- PMID: 39201368
- PMCID: PMC11354668
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168681
Virtual Screening and Validation of Affinity DNA Functional Ligands for IgG Fc Segment
Abstract
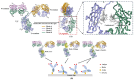
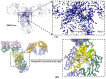
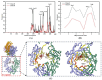
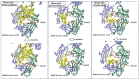
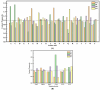
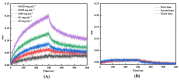
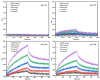
The effective attachment of antibodies to the immune sensing interface is a crucial factor that determines the detection performance of immunosensors. Therefore, this study aims to investigate a novel antibody immobilization material with low molecular weight, high stability, and excellent directional immobilization effect. In this study, we employed molecular docking technology based on the ZDOCK algorithm to virtually screen DNA functional ligands (DNAFL) for the Fc segment of antibodies. Through a comprehensive analysis of the key binding sites and contact propensities at the interface between DNAFL and IgG antibody, we have gained valuable insights into the affinity relationship, as well as the principles governing amino acid and nucleotide interactions at this interface. Furthermore, molecular affinity experiments and competitive binding experiments were conducted to validate both the binding ability of DNAFL to IgG antibody and its actual binding site. Through affinity experiments using multi-base sequences, we identified bases that significantly influence antibody-DNAFL binding and successfully obtained DNAFL with an enhanced affinity towards the IgG Fc segment. These findings provide a theoretical foundation for the targeted design of higher-affinity DNAFLs while also presenting a new technical approach for immunosensor preparation with potential applications in biodetection.
Keywords: DNA functional ligand; Fc segment; affinity; molecular docking; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular insights into the binding selectivity of a synthetic ligand DAAG to Fc fragment of IgG.J Mol Recognit. 2014 May;27(5):250-9. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2356. J Mol Recognit. 2014. PMID: 24700592
-
Structural mechanism of high affinity FcγRI recognition of immunoglobulin G.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):192-200. doi: 10.1111/imr.12346. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497521 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of hydrophobic charge-induction chromatography: interactions between the immobilized 4-mercaptoethyl-pyridine ligand and IgG.J Chromatogr A. 2012 Oct 19;1260:143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.08.080. Epub 2012 Aug 29. J Chromatogr A. 2012. PMID: 22975355
-
An improved Protein G with higher affinity for human/rabbit IgG Fc domains exploiting a computationally designed polar network.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2014 Apr;27(4):127-34. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzu005. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2014. PMID: 24632761 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of Fc/FcγR complexes: a blueprint for antibody design.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):201-21. doi: 10.1111/imr.12365. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497522 Review.
References
-
- Jiang C., Mu X., Du B., Tong Z. A Review of Electrochemical Biosensor Application in the Detection of the SARS-COV-2. Micro Nano Lett. 2022;17:49–58. doi: 10.1049/mna2.12101. - DOI
-
- Negahdary M., Angnes L. Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of microRNAs (miRNAs) Related to Cancer. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022;464:214565. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214565. - DOI
-
- Dostalova S., Cerna T., Hynek D., Koudelkova Z., Vaculovic T., Kopel P., Hrabeta J., Heger Z., Vaculovicova M., Eckschlager T., et al. Site-Directed Conjugation of Antibodies to Apoferritin Nanocarrier for Targeted Drug Delivery to Prostate Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2016;8:14430–14441. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b04286. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

