Activation of ARP2/3 and HSP70 Expression by Lipoteichoic Acid: Potential Bidirectional Regulation of Apoptosis in a Mastitis Inflammation Model
- PMID: 39199289
- PMCID: PMC11352453
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14080901
Activation of ARP2/3 and HSP70 Expression by Lipoteichoic Acid: Potential Bidirectional Regulation of Apoptosis in a Mastitis Inflammation Model
Abstract
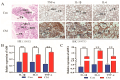
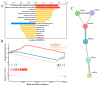
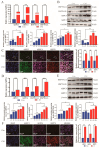
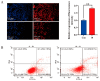
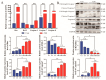
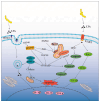
Mastitis typically arises from bacterial invasion, where host cell apoptosis significantly contributes to the inflammatory response. Gram-positive bacteria predominantly utilize the virulence factor lipoteichoic acid (LTA), which frequently leads to chronic breast infections, thereby impacting dairy production and animal husbandry adversely. This study employed LTA to develop models of mastitis in cow mammary gland cells and mice. Transcriptomic analysis identified 120 mRNAs associated with endocytosis and apoptosis pathways that were enriched in the LTA-induced inflammation of the Mammary Alveolar Cells-large T antigen (MAC-T), with numerous differential proteins also concentrated in the endocytosis pathway. Notably, actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 3 (ARPC3), actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 (ARPC4), and the heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) are closely related. STRING analysis revealed interactions among ARPC3, ARPC4, and HSP70 with components of the apoptosis pathway. Histological and molecular biological assessments confirmed that ARPC3, ARPC4, and HSP70 were mainly localized to the cell membrane of mammary epithelial cells. ARPC3 and ARPC4 are implicated in the mechanisms of bacterial invasion and the initiation of inflammation. Compared to the control group, the expression levels of these proteins were markedly increased, alongside the significant upregulation of apoptosis-related factors. While HSP70 appears to inhibit apoptosis and alleviate inflammation, its upregulation presents novel research opportunities. In conclusion, we deduced the development mechanism of ARPC3, ARPC4, and HSP70 in breast inflammation, laying the foundation for further exploring the interaction mechanism between the actin-related protein 2/3 (ARP2/3) complex and HSP70.
Keywords: ARPC3/4; HSP70; apoptosis; lipoteichoic acid; mastitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PGN and LTA from Staphylococcus aureus Induced Inflammation and Decreased Lactation through Regulating DNA Methylation and Histone H3 Acetylation in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 9;12(4):238. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040238. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32283626 Free PMC article.
-
The Synergism of PGN, LTA and LPS in Inducing Transcriptome Changes, Inflammatory Responses and a Decrease in Lactation as Well as the Associated Epigenetic Mechanisms in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jun 11;12(6):387. doi: 10.3390/toxins12060387. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545333 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Peptidoglycan, Lipoteichoic Acid and Lipopolysaccharide on Inflammation, Proliferation and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 2;12(8):497. doi: 10.3390/toxins12080497. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32748871 Free PMC article.
-
TRIENNIAL LACTATION SYMPOSIUM/BOLFA: Pathogen-specific immune response and changes in the blood-milk barrier of the bovine mammary gland.J Anim Sci. 2017 Dec;95(12):5720-5728. doi: 10.2527/jas2017.1845. J Anim Sci. 2017. PMID: 29293747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome sequencing analysis of bovine mammary epithelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharide.Anim Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;35(1):2290527. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2023.2290527. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Anim Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38141161 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

