FGF1 Suppresses Allosteric Activation of β3 Integrins by FGF2: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Thrombotic Action of FGF1
- PMID: 39199276
- PMCID: PMC11351609
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14080888
FGF1 Suppresses Allosteric Activation of β3 Integrins by FGF2: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Thrombotic Action of FGF1
Abstract
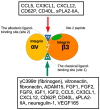
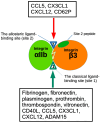
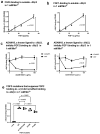
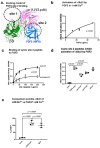
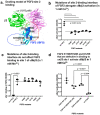
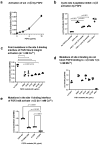
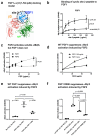
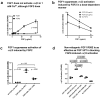
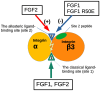
Several inflammatory cytokines bind to the allosteric site (site 2) and allosterically activate integrins. Site 2 is also a binding site for 25-hydroxycholesterol, an inflammatory lipid mediator, and is involved in inflammatory signaling (e.g., TNF and IL-6 secretion) in addition to integrin activation. FGF2 is pro-inflammatory and pro-thrombotic, and FGF1, homologous to FGF2, has anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic actions, but the mechanism of these actions is unknown. We hypothesized that FGF2 and FGF1 bind to site 2 of integrins and regulate inflammatory signaling. Here, we describe that FGF2 is bound to site 2 and allosterically activated β3 integrins, suggesting that the pro-inflammatory action of FGF2 is mediated by binding to site 2. In contrast, FGF1 bound to site 2 but did not activate these integrins and instead suppressed integrin activation induced by FGF2, indicating that FGF1 acts as an antagonist of site 2 and that the anti-inflammatory action of FGF1 is mediated by blocking site 2. A non-mitogenic FGF1 mutant (R50E), which is defective in binding to site 1 of αvβ3, suppressed β3 integrin activation by FGF2 as effectively as WT FGF1.
Keywords: FGF1; FGF2; anti-inflammatory action; anti-thrombotic action; integrin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The integrin-binding defective FGF2 mutants potently suppress FGF2 signalling and angiogenesis.Biosci Rep. 2017 Apr 10;37(2):BSR20170173. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170173. Print 2017 Apr 28. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28302677 Free PMC article.
-
A dominant-negative FGF1 mutant (the R50E mutant) suppresses tumorigenesis and angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057927. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469107 Free PMC article.
-
A novel fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF1) mutant that acts as an FGF antagonist.PLoS One. 2010 Apr 21;5(4):e10273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010273. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20422052 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Screening of Protein Data Bank via Docking Simulation Identified the Role of Integrins in Growth Factor Signaling, the Allosteric Activation of Integrins, and P-Selectin as a New Integrin Ligand.Cells. 2023 Sep 13;12(18):2265. doi: 10.3390/cells12182265. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37759488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Control of the intracellular signaling induced by fibroblast growth factors (FGF) over the proliferation and survival of retinal pigment epithelium cells: example of the signaling regulation of growth factors endogenous to the retina ].J Soc Biol. 2001;195(2):101-6. J Soc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11723820 Review. French.

