Label-Free Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy with Machine Learning for the Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer by Using Fine-Needle Aspiration Liquid Samples
- PMID: 39194601
- PMCID: PMC11352209
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14080372
Label-Free Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy with Machine Learning for the Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer by Using Fine-Needle Aspiration Liquid Samples
Abstract
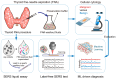
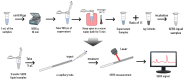
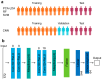
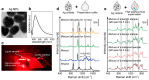
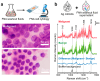
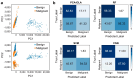
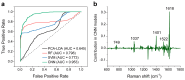
The incidence of thyroid cancer is increasing worldwide. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology is widely applied with the use of extracted biological cell samples, but current FNA cytology is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and can lead to the risk of false-negative results. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined with machine learning algorithms holds promise for cancer diagnosis. In this study, we develop a label-free SERS liquid biopsy method with machine learning for the rapid and accurate diagnosis of thyroid cancer by using thyroid FNA washout fluids. These liquid supernatants are mixed with silver nanoparticle colloids, and dispersed in quartz capillary for SERS measurements to discriminate between healthy and malignant samples. We collect Raman spectra of 36 thyroid FNA samples (18 malignant and 18 benign) and compare four classification models: Principal Component Analysis-Linear Discriminant Analysis (PCA-LDA), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The results show that the CNN algorithm is the most precise, with a high accuracy of 88.1%, sensitivity of 87.8%, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.953. Our approach is simple, convenient, and cost-effective. This study indicates that label-free SERS liquid biopsy assisted by deep learning models holds great promise for the early detection and screening of thyroid cancer.
Keywords: CNN; Raman spectroscopy; liquid biopsy; machine learning; thyroid fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Filter-Membrane-Based Ultrafiltration Coupled with Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Potential Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Thyroid Tumors from Blood Plasma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Apr 1;15:2303-2314. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S233663. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32280222 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-assisted internal standard calibration label-free SERS strategy for colon cancer detection.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Apr;415(9):1699-1707. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04566-1. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36781448
-
Serum analysis based on SERS combined with 2D convolutional neural network and Gramian angular field for breast cancer screening.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024 May 5;312:124054. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2024.124054. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024. PMID: 38382221
-
Analysis and comparison of machine learning methods for blood identification using single-cell laser tweezer Raman spectroscopy.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022 Sep 5;277:121274. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2022.121274. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022. PMID: 35500354 Review.
-
Cancer diagnosis using label-free SERS-based exosome analysis.Theranostics. 2024 Feb 24;14(5):1966-1981. doi: 10.7150/thno.92621. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38505618 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

