Alzheimer's disease CSF biomarkers correlate with early pathology and alterations in neuronal and glial gene expression
- PMID: 39192661
- PMCID: PMC11485399
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14194
Alzheimer's disease CSF biomarkers correlate with early pathology and alterations in neuronal and glial gene expression
Abstract
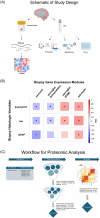
Introduction: Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) patients undergoing cortical shunting frequently show early Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology on cortical biopsy, which is predictive of progression to clinical AD. The objective of this study was to use samples from this cohort to identify cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers for AD-related central nervous system (CNS) pathophysiologic changes using tissue and fluids with early pathology, free of post mortem artifact.
Methods: We analyzed Simoa, proteomic, and metabolomic CSF data from 81 patients with previously documented pathologic and transcriptomic changes.
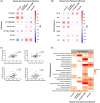
Results: AD pathology on biopsy correlates with CSF β-amyloid-42/40, neurofilament light chain (NfL), and phospho-tau-181(p-tau181)/β-amyloid-42, while several gene expression modules correlate with NfL. Proteomic analysis highlights seven core proteins that correlate with pathology and gene expression changes on biopsy, and metabolomic analysis of CSF identifies disease-relevant groups that correlate with biopsy data.
Discussion: As additional biomarkers are added to AD diagnostic panels, our work provides insight into the CNS pathophysiology these markers are tracking.
Highlights: AD CSF biomarkers correlate with CNS pathology and transcriptomic changes. Seven proteins correlate with CNS pathology and gene expression changes. Inflammatory and neuronal gene expression changes correlate with YKL-40 and NPTXR, respectively. CSF metabolomic analysis identifies pathways that correlate with biopsy data. Fatty acid metabolic pathways correlate with β-amyloid pathology.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; CSF; biomarkers; metabolomics; proteomics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
L.S.H. reports grants from NIH, New York State Dept of Health, Lewy Body Disease Association, CurePSP, Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Biogen, Bristol‐Myer Squibb, Cognition, EIP, Eisai, Genentech/Roche, Janssen/Johnson and Johnson, Transposon Therapeutics, UCB, and Vaccinex, as well as consulting fees from Biogen, Corium, Eisai, Genentech/Roche, and New Amsterdam, Payment or honoraria from Eisai Pharmaceuticals, Medscape, and Biogen, Payment for expert testimony from Monsanto and legal firms, support for attending meetings and/or travel from Eisai Pharmaceuticals, participation on a data safety monitoring or advisory board from Prevail Therapeutics/Lilly, Cortexyme, and Eisai, and a leadership role in the Alzheimer's Association. G.W.M. reports grant funding from NIH, CancerUK, Department of Defense (USAMRAA), Alley Corp, and SPARK‐NS. A.F.T. reports grant funding from NIH and Regeneron, stock ownership in Biogen and Ionis, paid committee work for DOD and NIH, and unpaid committee work for the Alzheimer's Association. R.A.M. reports grants from NIH, Minnesota Partnership for Biotechnology and Genomics, Minnesota Robotics Institute, and MnDRIVE Data Science Initiative. G.M.M. reports grants from NIH, consulting with Koh Young Inc and NeuroOne Technologies, participation on the Medronic SLATE trial Publication Committee, and leadership/committee roles in the Neurosurgical Society of America, AANS, and ASSFN. L.M.B. reports support from NIH. The other authors have nothing to report. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures

Update of
-
Alzheimer's disease CSF biomarkers correlate with early pathology and alterations in neuronal and glial gene expression.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 13:2024.06.11.24308706. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.11.24308706. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):7090-7103. doi: 10.1002/alz.14194 PMID: 38947015 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's disease CSF biomarkers correlate with early pathology and alterations in neuronal and glial gene expression.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 13:2024.06.11.24308706. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.11.24308706. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):7090-7103. doi: 10.1002/alz.14194 PMID: 38947015 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Time Trends of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;80(4):1629-1642. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201361. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33720890 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased cerebrospinal fluid neuronal pentraxin receptor is associated with PET-Aβ load and cerebrospinal fluid Aβ in a pilot study of Alzheimer's disease.Neurosci Lett. 2020 Jul 13;731:135078. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135078. Epub 2020 May 23. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 32450185
-
CSF proteomic profiles of neurodegeneration biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Sep;20(9):6205-6220. doi: 10.1002/alz.14103. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38970402 Free PMC article.
-
New fluid biomarkers tracking non-amyloid-β and non-tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Apr;52(4):556-568. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0418-9. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32284537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borgesen SE, Gjerris F. The predictive value of conductance to outflow of CSF in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain. 1982;105:65‐86. - PubMed
-
- Symon L, Dorsch NW. Use of long‐term intracranial pressure measurement to assess hydrocephalic patients prior to shunt surgery. J Neurosurg. 1975;42:258‐273. - PubMed
-
- McGovern RA, Nelp TB, Kelly KM, et al. Predicting cognitive improvement in normal pressure hydrocephalus patients using preoperative neuropsychological testing and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Neurosurgery. 2019;85:E662‐E669. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

