Mitochondrial dysfunction in acute kidney injury
- PMID: 39192578
- PMCID: PMC11360640
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2393262
Mitochondrial dysfunction in acute kidney injury
Abstract
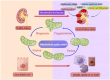
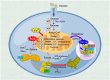
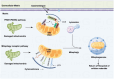
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a systemic clinical syndrome increasing morbidity and mortality worldwide in recent years. Renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) death caused by mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the pathogeneses. The imbalance of mitochondrial quality control is the main cause of mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrial quality control plays a crucial role in AKI. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms are involved in regulating mitochondrial integrity and function, including antioxidant defense, mitochondrial quality control, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) repair, mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis. Currently, many studies have used mitochondrial dysfunction as a targeted therapeutic strategy for AKI. Therefore, this review aims to present the latest research advancements on mitochondrial dysfunction in AKI, providing a valuable reference and theoretical foundation for clinical prevention and treatment of this condition, ultimately enhancing patient prognosis.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; mitochondrial biogenesis; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial quality control; mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The figures in the manuscript were drawn in Figdraw.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondria as therapeutic targets in acute kidney injury.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Jul;25(4):355-62. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000228. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27166518 Review.
-
Drp1-dependent mitophagy protects against cisplatin-induced apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells by improving mitochondrial function.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):20988-21000. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15470. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423497 Free PMC article.
-
Indispensable role of mitochondria in maintaining the therapeutic potential of curcumin in acute kidney injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(20):9863-9877. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16934. Epub 2021 Sep 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34532973 Free PMC article.
-
Fundc1-dependent mitophagy is obligatory to ischemic preconditioning-conferred renoprotection in ischemic AKI via suppression of Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission.Redox Biol. 2020 Feb;30:101415. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101415. Epub 2019 Dec 28. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 31901590 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and the AKI-to-CKD transition.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):F1105-F1116. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00285.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33073587 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
