Emerging approaches for the development of artificial islets
- PMID: 39188698
- PMCID: PMC11235711
- DOI: 10.1002/SMMD.20230042
Emerging approaches for the development of artificial islets
Abstract
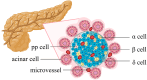
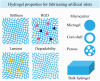
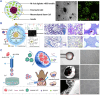
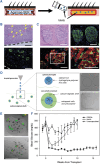
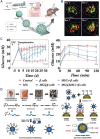
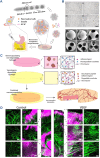
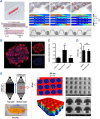
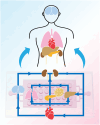
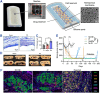
The islet of Langerhans, functioning as a "mini organ", plays a vital role in regulating endocrine activities due to its intricate structure. Dysfunction in these islets is closely associated with the development of diabetes mellitus (DM). To offer valuable insights for DM research and treatment, various approaches have been proposed to create artificial islets or islet organoids with high similarity to natural islets, under the collaborative effort of biologists, clinical physicians, and biomedical engineers. This review investigates the design and fabrication of artificial islets considering both biological and tissue engineering aspects. It begins by examining the natural structures and functions of native islets and proceeds to analyze the protocols for generating islets from stem cells. The review also outlines various techniques used in crafting artificial islets, with a specific focus on hydrogel-based ones. Additionally, it provides a concise overview of the materials and devices employed in the clinical applications of artificial islets. Throughout, the primary goal is to develop artificial islets, thereby bridging the realms of developmental biology, clinical medicine, and tissue engineering.
Keywords: artificial islet; diabetes; hydrogel; microfluidics; regenerative medicine.
© 2024 The Authors. Smart Medicine published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A hydrogel platform for in vitro three dimensional assembly of human stem cell-derived islet cells and endothelial cells.Acta Biomater. 2019 Oct 1;97:272-280. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.08.031. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31446050 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty years of islet-on-a-chip: microfluidic tools for dissecting islet metabolism and function.Lab Chip. 2024 Feb 27;24(5):1327-1350. doi: 10.1039/d3lc00696d. Lab Chip. 2024. PMID: 38277011 Review.
-
Pancreatic islet organoids-on-a-chip: how far have we gone?J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jun 28;20(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01518-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35764957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Making human pancreatic islet organoids: Progresses on the cell origins, biomaterials and three-dimensional technologies.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 3;12(4):1537-1556. doi: 10.7150/thno.66670. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35198056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Islet organoid as a promising model for diabetes.Protein Cell. 2022 Apr;13(4):239-257. doi: 10.1007/s13238-021-00831-0. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Protein Cell. 2022. PMID: 33751396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced glycation end products mediate biomineralization disorder in diabetic bone disease.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Sep 17;5(9):101694. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101694. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39173634 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

