Engineered extracellular vesicles coated with an antimicrobial peptide for advanced control of bacterial sepsis
- PMID: 39185334
- PMCID: PMC11342353
- DOI: 10.1002/jex2.70000
Engineered extracellular vesicles coated with an antimicrobial peptide for advanced control of bacterial sepsis
Abstract
Alarming sepsis-related mortality rates present significant challenges to healthcare services globally. Despite advances made in the field, there is still an urgent need to develop innovative approaches that could improve survival rates and reduce the overall cost of treatment for sepsis patients. Therefore, this study aimed to develop a novel multifunctional therapeutic agent for advanced control of bacterial sepsis. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) isolated from lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced HepG2 (hepatocellular carcinoma cells) (iEV) displayed an average particle size of 171.63 ± 2.77 nm, a poly dispersion index (PDI) of 0.32 ± 0.0, and a zeta potential (ZP) of -11.87 ± 0.18 mV. Compared to HepG2 EV, LPS induction significantly increases the EV protein concentration, PDI and ZP, reduces the average size and promotes cell proliferation and cytoprotective effects of the isolated EVs (iEVs) against LPS-induced cytotoxicity. Coating of iEV with a cationic antimicrobial peptide (AMP) to form PC-iEV slightly changed their physical properties and shifted their surface charge toward neutral values. This modification improved the antibacterial activity (2-fold lower minimum bactericidal concentration [MBC] values) and biocompatibility of the conjugated peptide while maintaining iEV cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory activities. Our findings indicate the superior anti-inflammatory and antibacterial dual activity of PC-iEV against pathogens associated with sepsis.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides: extracellular vesicles; sepsis; therapeutics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Biology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

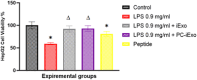
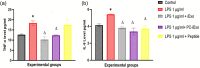
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of MAF-1-Derived Antimicrobial Peptide Mt6 and Its D-Enantiomer D-Mt6 against Acinetobacter baumannii by Targeting Cell Membranes and Lipopolysaccharide Interaction.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0131222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01312-22. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36190276 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Fusion Protein BPI21/LL-37 Modification Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of hUC-MSCs in Sepsis.Mol Ther. 2020 Aug 5;28(8):1806-1817. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.05.014. Epub 2020 May 15. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32445625 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Cathelicidin Peptide LL-37, an Antimicrobial Agent, in a Murine Sepsis Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 19;21(17):5973. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175973. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan Nanoparticles Against Pathogenic N. gonorrhoea.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 13;15:7877-7887. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S272736. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33116506 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides with dual mode of action: Killing bacteria and preventing endotoxin-induced sepsis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1858(5):971-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26801369 Review.
References
-
- Abdel‐Rahman, I. M. , Mustafa, M. , Mohamed, S. A. , Yahia, R. , Abdel‐Aziz, M. , Abuo‐Rahma, G. E.‐D. A. , & Hayallah, A. M. (2021). Novel Mannich bases of ciprofloxacin with improved physicochemical properties, antibacterial, anticancer activities and caspase‐3 mediated apoptosis. Bioorganic Chemistry, 107, 104629. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104629 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abou‐Yousef, H. , Dacrory, S. , Hasanin, M. , Saber, E. , & Kamel, S. (2021). Biocompatible hydrogel based on aldehyde‐functionalized cellulose and chitosan for potential control drug release. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 21, 100419. 10.1016/j.scp.2021.100419 - DOI
-
- Ahadi, H. , Shokrzadeh, M. , Hosseini‐khah, Z. , Ghassemi barghi, N. , Ghasemian, M. , Emadi, E. , Zargari, M. , Razzaghi‐Asl, N. , & Emami, S. (2020). Synthesis and biological assessment of ciprofloxacin‐derived 1,3,4‐thiadiazoles as anticancer agents. Bioorganic Chemistry, 105, 104383. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104383 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, M. L. , Khosroheidari, M. , Ravi, R. K. , & DiStefano, J. K. (2012). Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney International, 82(9), 1024–1032. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
