A novel bakuchiol aminoguanidine derivative induces apoptosis in human triple-negative breast cancer cells
- PMID: 39183056
- PMCID: PMC11375495
- DOI: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2024-0070
A novel bakuchiol aminoguanidine derivative induces apoptosis in human triple-negative breast cancer cells
Abstract
Objectives: To synthesize new bakuchiol aminoguanidine derivatives and test their effect on viability and apoptosis of human triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells.
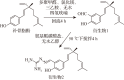
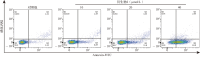
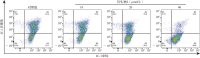
Methods: Two bakuchiol derivatives 1 and 2 were obtained by formylation and Shiff base reaction of bakuchol. The structures of derivatives 1 and 2 were identified by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, and high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS) analysis. Human TNBC MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with bakuchiol and its derivatives and cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Apoptosis was detected by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry with Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. The expressions of apoptosis-related proteins were analyzed with Western blotting. The JC-1 and reactive oxygen species (ROS) assay kits were used to determine the effect of new bakuchiol derivatives on mitochondrial function.
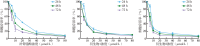
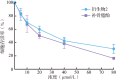
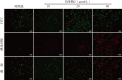
Results: Based on spectroscopic analysis, a new bakuchiol schiff base derivative was elucidated as 2-{(E)-5-[(S, E)-3, 7-dimethyl-3-vinylocta-1, 6-dien-1-yl]-2-hydroxylbenzylidene} hydrazine-1-carboximidamide (derivative 2). Bakuchiol and its derivatives 1 and 2 all showed cytotoxic activity against the MDA-MB-231 cells. Derivative 2 exhibited the most potent cytotoxic activity to MDA-MB-231 cell with IC50 of (13.11±1.09), (6.91±1.78), and (2.23±1.32) μmol/L after 24, 48, and 72 h. It had low toxicity to normal mouse liver (AML-12) cells with IC50 of (31.23±1.58) μmol/L at 72 h. Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry demonstrated apoptosis in breast cancer cells after treating with derivative 2 in a concentration dependent manner. Western blotting showed that after derivative 2 treatment, the expression of apoptosis-related proteins cytochrome C, cleaving caspase-3 and Bax/Bcl-2 radio in MDA-MB-231 cells increased; in addition, apoptosis was associated with the decreased mitochondrial membrane potential and increased reactive oxygen species accumulation.
Conclusions: The novel bakuchiol aminoguanidine derivative (derivative 2) is capable of inducing apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells, but has low toxicity to normal liver cells, suggesting that it may be used as a lead compound for an anti-TNBC agent.
目的: 合成新型补骨脂酚氨基胍衍生物,并探讨其对人三阴性乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞死亡的影响。方法: 以补骨脂酚为起始化合物,通过甲酰化和席夫碱反应获得补骨脂酚衍生物1、2,并经氢谱、碳谱和高分辨质谱鉴定其结构;用噻唑蓝(MTT)法检测补骨脂酚及其衍生物对细胞存活率的影响;利用荧光显微镜、Anexxin V/PI双染结合流式细胞术法检测补骨脂酚及其衍生物对MDA-MB-231细胞凋亡的影响;蛋白质印迹法检测凋亡相关蛋白的表达;JC-1试剂盒检测细胞线粒体膜电位;DCFH-DA法检测细胞内的活性氧水平。结果: 根据波谱数据的分析,本研究合成获得1个新结构的补骨脂酚氨基胍衍生物,其化学名为2-{(E)-5- [(S,E)-3,7-dimethyl-3-vinylocta-1,6-dien-1-yl]-2-hydroxybenzylidene} hydrazine-1-carboximidamide(衍生物2)。MTT法结果显示,补骨脂酚及其衍生物对MDA-MB-231细胞均表现出一定的细胞毒性,其中衍生物2对MDA-MB-231细胞显示较强的细胞毒性,其作用24、48、72 h的IC50值分别为(13.11±1.09)、(6.91±1.78)和(2.23±1.32)μmol/L,但对小鼠正常肝细胞AML-12毒性较低,作用72 h的IC50值为(31.23±1.58)μmol/L。荧光显微镜下观察和流式细胞术检测结果显示,衍生物2诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡,且呈浓度依赖性。进一步研究发现,衍生物2作用后的MDA-MB-231细胞中Bax/Bcl-2比值增加,细胞色素C蛋白表达水平上调,胱天蛋白酶3激活,线粒体膜电位下降、细胞内活性氧水平显著增高。结论: 新型补骨脂酚氨基胍衍生物可诱导MDA-MB-231细胞发生凋亡,且对正常肝细胞的毒性较小,可作为抗三阴性乳腺癌的先导化合物。.
Keywords: Aminoguanidine; Apoptosis; Bakuchiol; Mitochondrial function; Triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel indole Schiff base β-diiminato compound as an anti-cancer agent against triple-negative breast cancer: In vitro anticancer activity evaluation and in vivo acute toxicity study.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Nov;152:107730. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107730. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39216194
-
Pyoluteorin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human triple-negative breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;72(7):969-978. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13262. Epub 2020 Apr 4. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32246778
-
Pyrazole Derivatives Induce Apoptosis via ROS Generation in the Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells, MDA-MB-468.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Jul 1;22(7):2079-2087. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.7.2079. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34319030 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in triple negative breast carcinoma cells by methylglyoxal via generation of reactive oxygen species.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Sep;56(9):2086-2103. doi: 10.1002/mc.22665. Epub 2017 May 22. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28418078
-
[Stellera chamaejasme against multidrug resistance of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell through Nrf2].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Apr;49(8):2222-2229. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20231212.704. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38812237 Chinese.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous