Prefrontal cortex molecular clock modulates development of depression-like phenotype and rapid antidepressant response in mice
- PMID: 39179578
- PMCID: PMC11344080
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51716-9
Prefrontal cortex molecular clock modulates development of depression-like phenotype and rapid antidepressant response in mice
Abstract
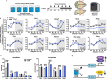
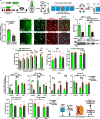
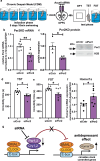
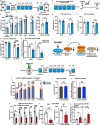
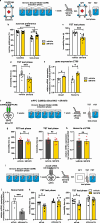
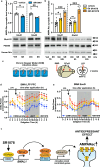
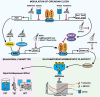
Depression is associated with dysregulated circadian rhythms, but the role of intrinsic clocks in mood-controlling brain regions remains poorly understood. We found increased circadian negative loop and decreased positive clock regulators expression in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of a mouse model of depression, and a subsequent clock countermodulation by the rapid antidepressant ketamine. Selective Bmal1KO in CaMK2a excitatory neurons revealed that the functional mPFC clock is an essential factor for the development of a depression-like phenotype and ketamine effects. Per2 silencing in mPFC produced antidepressant-like effects, while REV-ERB agonism enhanced the depression-like phenotype and suppressed ketamine action. Pharmacological potentiation of clock positive modulator ROR elicited antidepressant-like effects, upregulating plasticity protein Homer1a, synaptic AMPA receptors expression and plasticity-related slow wave activity specifically in the mPFC. Our data demonstrate a critical role for mPFC molecular clock in regulating depression-like behavior and the therapeutic potential of clock pharmacological manipulations influencing glutamatergic-dependent plasticity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.S. is an honoraria consulting and advisory board member of Primetime Life Sciences, LLC. C.N. received lecture fees and advisory board honoraria from Janssen-Cilag. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cortical and raphe GABAA, AMPA receptors and glial GLT-1 glutamate transporter contribute to the sustained antidepressant activity of ketamine.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 May;192:172913. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172913. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 32201299
-
IGF-1 release in the medial prefrontal cortex mediates the rapid and sustained antidepressant-like actions of ketamine.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 May 17;12(1):178. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01943-9. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35577782 Free PMC article.
-
Bisphenol A Alters Bmal1, Per2, and Rev-Erba mRNA and Requires Bmal1 to Increase Neuropeptide Y Expression in Hypothalamic Neurons.Endocrinology. 2019 Jan 1;160(1):181-192. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-00881. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30500912 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel circadian clock modulator controlling BMAL1 expression through a ROR/REV-ERB-response element-dependent mechanism.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jan 15;469(3):580-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.030. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26692477
-
Pharmacological targeting of the mammalian clock regulates sleep architecture and emotional behaviour.Nat Commun. 2014 Dec 23;5:5759. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6759. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25536025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. World Mental Health Report (World Health Organization, 2022).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

