Free radical fragmentation and oxidation in the polar part of lysophospholipids: Results of the study of blood serum of healthy donors and patients with acute surgical pathology
- PMID: 39178730
- PMCID: PMC11388268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103309
Free radical fragmentation and oxidation in the polar part of lysophospholipids: Results of the study of blood serum of healthy donors and patients with acute surgical pathology
Abstract
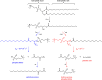
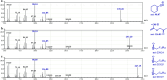
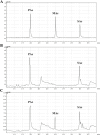
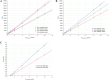
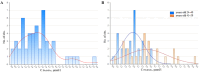
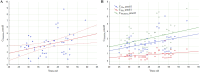
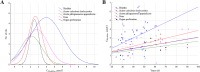
The interaction of reactive oxygen species with cell membrane lipids is usually considered in the context of lipid peroxidation in the nonpolar component of the membrane. In this work, for the first time, data were obtained indicating that damage to human cell membranes can occur in the polar part of lysophospholipids at the interface with the aqueous environment due to free radical fragmentation (FRF) processes. FRF products, namely 1-hexadecanoyloxyacetone (PAc) and 1-octadecanoyloxyacetone (SAc), were identified in human serum, and a GC-MS method was developed to quantify PAc and SAc. The content of FRF products in serum samples of 52 healthy donors was found to be in the range of 1.98-4.75 μmol/L. A linear regression equation, CPAc&SAc (μmol/L) = 0.51 + 0.064 × years, was derived to describe the relationship between age and content of FRF products. In 70 patients with acute surgical pathology in comparison with the control group of healthy donors, two distinct clusters with different concentration levels of FRF products were revealed. The first cluster: groups of 43 patients with various localized inflammatory-destructive lesions of hollow organ walls and bacterial translocation (septic inflammation) of abdominal cavity organs. These patients showed a 1.5-1.9-fold (p = 0.012) decrease in the total concentration of PAc and SAc in serum. In the second cluster: groups of 27 patients with ischemia-reperfusion tissue damage (aseptic inflammation), - a statistically significant increase in the concentration of FRF products was observed: in 2.2-4.0 times (p = 0.0001). The obtained data allow us to further understand the role of free-radical processes in the damage of lipid molecules. FRF products can potentially be used as markers of the degree of free-radical damage of hydroxyl containing phospholipids.
Keywords: Blood serum; Free radical fragmentation; Lysophosphatidylcholine; Palmitoxyacetone; Septic and aseptic inflammation; Stearoxyacetone.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest We are sending the manuscript (original research article) by Alexey Fedoruk, Oleg Shadyro. Irina Edimecheva, Dmitry Fedoruk, Valery Khrutskin, Leanid Kirkovsky, Viktor Sorokin, Halina Talkachova entitled « Free radical fragmentation and oxidation in the polar part of lysophospholipids: results of the study of blood serum of healthy donors and patients with acute surgical pathology » to be evaluated for publication in «Redox Biology». The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper. All authors have read the manuscript and concur with the submission, the work has not been published elsewhere, either completely, in part, or in another form, the manuscript has not been submitted to another journal and will not be published elsewhere.
Figures

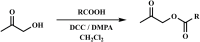
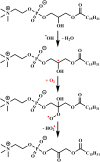
Similar articles
-
Influence of lipids with hydroxyl-containing head groups on Fe2+ (Cu2+)/H2O2-mediated transformation of phospholipids in model membranes.Chem Phys Lipids. 2014 Jan;177:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Chem Phys Lipids. 2014. PMID: 24189590
-
[Free oxygen radiacals and kidney diseases--part I].Med Pregl. 2000 Sep-Oct;53(9-10):463-74. Med Pregl. 2000. PMID: 11320727 Review. Croatian.
-
Free radical oxidation of polyunsaturated lipids: New mechanistic insights and the development of peroxyl radical clocks.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Jun 21;44(6):458-67. doi: 10.1021/ar200024c. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21486044 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced peroxidation and fragmentation of lipids in a model membrane.Int J Radiat Biol. 2002 Mar;78(3):211-7. doi: 10.1080/09553000110104065. Int J Radiat Biol. 2002. PMID: 11869476
-
Effects of pineal peptide preparation Epithalamin on free-radical processes in humans and animals.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2001;22(1):9-18. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11335874 Review.
References
-
- Sies Helmut. Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1986;25(12):1058–1071. doi: 10.1002/anie.198610581. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

