Poly (I:C) increases the expression of galectin 1, 3, 9 and HGF genes in exosomes isolated from human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 39170483
- PMCID: PMC11336598
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35343
Poly (I:C) increases the expression of galectin 1, 3, 9 and HGF genes in exosomes isolated from human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
Background: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are commonly employed as a powerful tool for the treatment of immune-mediated problems owing to their capacity to regulate the immune system and differentiate into different tissues. Researchers use mesenchymal stem cell products given the limitations associated with the application of MSCs. Exosomes are nanometer vesicles derived from MSCs that are used in cell-free therapy. Inflammatory environmental conditions, such as stimulation of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR-3), has the ability to adjust the immune-regulating properties and anti-inflammatory function of mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes. Galectins and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) are known as immunomodulatory factors in mesenchymal stem cells. This study was designed to examine the expression of galectin-1, galectin-3, galectin-9, and HGF genes in exosomes isolated from human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells (hWJ-MSCs) after stimulation with Poly (I:C) (Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid sodium salt).
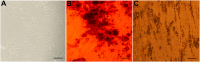
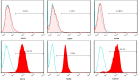
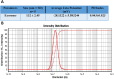
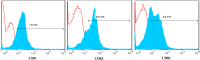
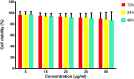
Methods: To begin, the explant technique was used to extract mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly. Then, the stem cells were stimulated using Poly (I:C) at three time intervals of 12, 24 and 48 h. Exosomes secreted from the supernatant of cells were extracted and exosome confirmation tests, including Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Dynamic light scattering (DLS) and Flow cytometry were performed. Finally, the expression of galectin-1, galectin-3, galectin-9, and HGF genes in exosomes was evaluated by Real-Time PCR at three time intervals of 12, 24 and 48 h after stimulation.
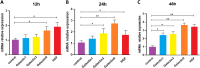
Results: The findings of our study indicated that following stimulation with Poly (I:C), the expression of galectin-9 and HGF (P < 0.05) genes was markedly higher than in the control group after 12 h. After 24 h, the expression of galectin-9 (P < 0.01), galectin-3 and HGF (P < 0.05) increased; the expression of galectin-1, galectin-3, (P < 0.05), galectin-9 and HGF genes (p < 0.01) significantly increased compared to the control group after 48 h.
Conclusion: TLR3 stimulation can increase the expression of galectins and HGF genes in exosomes derived from hWJ-MSCs and may be improve the immunosuppressive abilities of exosomes.
Keywords: Exosome; Galectin; Hepatocyte growth factor; Mesenchymal stem cells; Toll-like receptor 3.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Effect of Exosomes Isolated from Poly (I:C) Treated Human Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells on CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 May 27;23(3):288-298. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v23i3.15638. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39422388
-
Human umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into nerve-like cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Dec 5;118(23):1987-93. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. PMID: 16336835
-
[Expression of Galectins in umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Jun 18;45(3):452-7. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 23774927 Chinese.
-
Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell: Various Protocols for Isolation and Differentiation of Hepatocyte-Like Cells; Narrative Review.Iran J Med Sci. 2019 Nov;44(6):437-448. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2019.44952. Iran J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31875078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of mesenchymal stem cells derived from the umbilical cord or Wharton's jelly and their extracellular vesicles in the treatment of various diseases.Tissue Cell. 2024 Aug;89:102415. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2024.102415. Epub 2024 May 27. Tissue Cell. 2024. PMID: 38851032 Review.
References
-
- Okunishi K., Dohi M., Nakagome K., Tanaka R., Mizuno S., Matsumoto K., et al. A novel role of hepatocyte growth factor as an immune regulator through suppressing dendritic cell function. J. Immunol. 2005;175(7):4745–4753. - PubMed
-
- Carrade Holt D.D., Wood J.A., Granick J.L., Walker N.J., Clark K.C., Borjesson D.L. Equine mesenchymal stem cells inhibit T cell proliferation through different mechanisms depending on tissue source. Stem cells Dev. 2014;23(11):1258–1265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

