Association between albumin-bilirubin score and in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis: Evidence from two large databases
- PMID: 39170393
- PMCID: PMC11336323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34697
Association between albumin-bilirubin score and in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis: Evidence from two large databases
Abstract
Background: The Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) score, recommended for assessing the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients, has garnered attention. The efficacy of ALBI score in forecasting the risk of death in sepsis patients remains limited. We designed two cohort studies to assess the association between ALBI score and in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis.
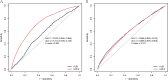
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted utilizing data from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University and the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV(MIMIC-IV). Patients diagnosed with sepsis were included in the analysis. The primary outcome was the in-hospital mortality. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was conducted to assess the independent association between the ALBI score and mortality, with adjustment for potential confounders. Subgroup analysis was conducted to assess the robustness of the findings.
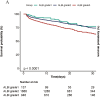
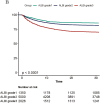
Results: The Guangzhou Sepsis Cohort (GZSC) of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University comprised 2969 participants, while the MIMIC-IV database included 8841 participants. The ALBI score were categorized into < -2.60, -2.60∼-1.39, and >-1.39. After adjusting for confounders, a linear relationship was observed between ALBI score and mortality. Patients with a high ALBI grade were associated with higher in-hospital mortality in both the GZSC (HR: 1.52, 95%CI: 1.24-1.87, p < 0.001) and the MIMIC-IV database (HR: 1.57, 95%CI: 1.46-1.70, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: A high ALBI score is associated with higher in-hospital mortality among sepsis patients in ICU.
Keywords: Albumin; Albumin-bilirubin; Bilirubin; In-hospital mortality; epsis.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A positive correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase level and in-hospital mortality in ICU sepsis patients: evidence from two large databases.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Nov 1;29(1):525. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02071-4. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39487549 Free PMC article.
-
ALBI Grade Is Associated with Clinical Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients with AKI: A Cohort Study with Cox Regression and Propensity Score Matching.Mediators Inflamm. 2024 Jul 18;2024:1412709. doi: 10.1155/2024/1412709. eCollection 2024. Mediators Inflamm. 2024. PMID: 39055134 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative albumin-bilirubin grade combined with aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet count ratio index predict outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria after liver resection.Biosci Trends. 2019 May 12;13(2):176-181. doi: 10.5582/bst.2019.01088. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Biosci Trends. 2019. PMID: 31061272
-
Prognostic impact of albumin-bilirubin score on the prediction of in-hospital mortality in patients with heart failure: a retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2022 Jan 4;12(1):e049325. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049325. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 34983753 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of preoperative albumin-bilirubin score in posthepatectomy liver failure and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Updates Surg. 2022 Jun;74(3):821-831. doi: 10.1007/s13304-021-01080-w. Epub 2021 May 19. Updates Surg. 2022. PMID: 34013432 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

