Fibroblast Growth Factors in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 39168622
- PMCID: PMC11537794
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.RV22025
Fibroblast Growth Factors in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
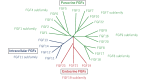
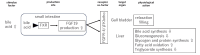
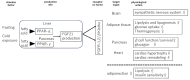
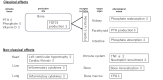
Despite advancements in managing traditional cardiovascular risk factors, many cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) persist. Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) have emerged as potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for CVDs. FGF1, FGF2, and FGF4 are primarily used for therapeutic angiogenesis. Clinical applications are being explored based on animal studies using approaches such as recombinant protein administration and adenovirus-mediated gene delivery, targeting patients with coronary artery disease and lower extremity arterial disease. Although promising results have been observed in animal models and early-stage clinical trials, further studies are required to assess their therapeutic potential. The FGF19 subfamily, consisting of FGF19, FGF21, and FGF23, act via endocrine signaling in various organs. FGF19, primarily expressed in the small intestine, plays important roles in glucose, lipid, and bile acid metabolism and has therapeutic potential for metabolic disorders. FGF21, found in various tissues, improves glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, suggesting potential for treating obesity and diabetes. FGF23, primarily secreted by osteocytes, regulates vitamin D and phosphate metabolism and serves as an important biomarker for chronic kidney disease and CVDs. Thus, FGFs holds promise for both therapeutic and diagnostic applications in metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the mechanisms of FGF may pave the way for novel strategies to prevent and manage CVDs, potentially addressing the limitations of current treatments. This review explores the roles of FGF1, FGF2, FGF4, and the FGF19 subfamily in maintaining cardiovascular health. Further research and clinical trials are crucial to fully understand the therapeutic potential of FGFs in managing cardiovascular health.
Keywords: Atherosoclerosis; Cardiometabolic regulation; Cardiovascular disease; Fibroblast growth factors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endocrine fibroblast growth factors as potential biomarkers for chronic kidney disease.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020 Jul;20(7):715-724. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2020.1780918. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020. PMID: 32513031 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of the endocrine fibroblast growth factors FGF19, FGF21 and FGF23.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Jan;15(1):51-69. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2015.9. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 26567701 Review.
-
Endocrine fibroblast growth factors in domestic animals.Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2024 Oct;89:106872. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2024.106872. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39059301 Review.
-
The Role of the FGF19 Family in the Pathogenesis of Gestational Diabetes: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 9;24(24):17298. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417298. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Changes in Circulating Endocrine FGF19 Subfamily and Fetuin-A in Response to Intralipid and Insulin Infusions in Healthy and PCOS Women.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 30;11:568500. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.568500. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33101202 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, Barengo NC, Beaton AZ, Benjamin EJ, Benziger CP, Bonny A, Brauer M, Brodmann M, Cahill TJ, Carapetis J, Catapano AL, Chugh SS, Cooper LT, Coresh J, Criqui M, DeCleene N, Eagle KA, Emmons-Bell S, Feigin VL, Fernández-Solà J, Fowkes G, Gakidou E, Grundy SM, He FJ, Howard G, Hu F, Inker L, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Koroshetz W, Lavie C, Lloyd-Jones D, Lu HS, Mirijello A, Temesgen AM, Mokdad A, Moran AE, Muntner P, Narula J, Neal B, Ntsekhe M, Moraes de Oliveira G, Otto C, Owolabi M, Pratt M, Rajagopalan S, Reitsma M, Ribeiro ALP, Rigotti N, Rodgers A, Sable C, Shakil S, Sliwa-Hahnle K, Stark B, Sundström J, Timpel P, Tleyjeh IM, Valgimigli M, Vos T, Whelton PK, Yacoub M, Zuhlke L, Murray C, and Fuster V: Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020; 76: 2982-3021 - PMC - PubMed

