Therapeutic biomaterials with liver X receptor agonists based on the horizon of material biology to regulate atherosclerotic plaque regression in situ for devices surface engineering
- PMID: 39165884
- PMCID: PMC11335375
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbae089
Therapeutic biomaterials with liver X receptor agonists based on the horizon of material biology to regulate atherosclerotic plaque regression in situ for devices surface engineering
Abstract
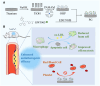
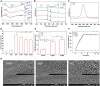
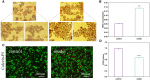
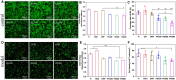
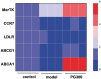
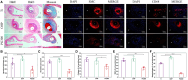
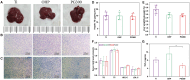
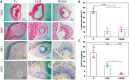
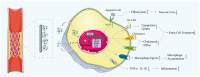
Percutaneous coronary interventional is the main treatment for coronary atherosclerosis. At present, most studies focus on blood components and smooth muscle cells to achieve anticoagulation or anti-proliferation effects, while the mediated effects of materials on macrophages are also the focus of attention. Macrophage foam cells loaded with elevated cholesterol is a prominent feature of atherosclerotic plaque. Activation of liver X receptor (LXR) to regulate cholesterol efflux and efferocytosis and reduce the number of macrophage foam cells in plaque is feasible for the regression of atherosclerosis. However, cholesterol efflux promotion remains confined to targeted therapies. Herein, LXR agonists (GW3965) were introduced on the surface of the material and delivered in situ to atherogenic macrophages to improve drug utilization for anti-atherogenic therapy and plaque regression. LXR agonists act as plaque inhibition mediated by multichannel regulation macrophages, including lipid metabolism (ABCA1, ABCG1 and low-density lipoprotein receptor), macrophage migration (CCR7) and efferocytosis (MerTK). Material loaded with LXR agonists significantly reduced plaque burden in atherosclerotic model rats, most importantly, it did not cause hepatotoxicity and adverse reactions such as restenosis and thrombosis after material implantation. Both in vivo and in vitro evaluations confirmed its anti-atherosclerotic capability and safety. Overall, multi-functional LXR agonist-loaded materials with pathological microenvironment regulation effect are expected to be promising candidates for anti-atherosclerosis and have potential applications in cardiovascular devices surface engineering.
Keywords: LXR agonists; atherosclerosis; devices surface engineering; macrophage; material-biology; pathological microenvironment-regulation; therapeutic biomaterials.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stimulation of cholesterol efflux by LXR agonists in cholesterol-loaded human macrophages is ABCA1-dependent but ABCG1-independent.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Nov;29(11):1930-6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.194548. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19729607
-
Activation of liver X receptor decreases atherosclerosis in Ldlr⁻/⁻ mice in the absence of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in myeloid cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Feb;34(2):279-84. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302781. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24311381 Free PMC article.
-
Sonodynamic therapy-induced foam cells apoptosis activates the phagocytic PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1/ABCG1 pathway and promotes cholesterol efflux in advanced plaque.Theranostics. 2018 Sep 29;8(18):4969-4984. doi: 10.7150/thno.26193. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30429880 Free PMC article.
-
Liver X receptor: a potential target in the treatment of atherosclerosis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022 Jul;26(7):645-658. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2022.2117610. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022. PMID: 36003057 Review.
-
Targeting macrophages in atherosclerosis using nanocarriers loaded with liver X receptor agonists: A narrow review.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Mar 2;10:1147699. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1147699. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36936982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Song P, Fang Z, Wang H, Cai Y, Rahimi K, Zhu Y, Fowkes FGR, Fowkes FJI, Rudan I.. Global and regional prevalence, burden, and risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. Lancet Glob Health 2020;8:e721–9–e729. - PubMed
-
- Gori T, Polimeni A, Indolfi C, Räber L, Adriaenssens T, Münzel T.. Predictors of stent thrombosis and their implications for clinical practice. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019;16:243–56. - PubMed
-
- Liu T, Liu Y, Chen Y, Liu S, Maitz MF, Wang X, Zhang K, Wang J, Wang Y, Chen J, Huang N.. Immobilization of heparin/poly-l-lysine nanoparticles on dopamine-coated surface to create a heparin density gradient for selective direction of platelet and vascular cells behavior. Acta Biomater 2014;10:1940–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

